* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Reproduction
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
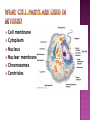
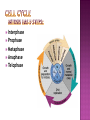
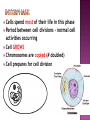
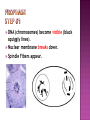
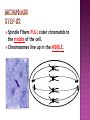
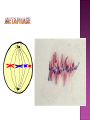
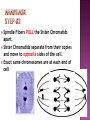
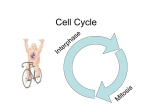
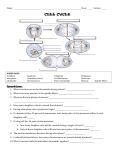
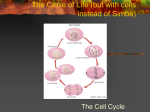
How do you grow? By cells dividing What happens when you fall on pavement? You scrapped your skin off New skin grows and replaces the old New cells are made to grow and repair the body through CELL REPRODUCTION Mitosis 2 identical cells are made from one cell. Body = cell reproduction of the body cells (like in your TOES). Cells: are cells that make up most of the body. Skin, bone, blood, stomach Most of the cell’s time is spent GROWING, dividing only happens a little. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Nuclear membrane Chromosomes Centrioles Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cells spend most of their life in this phase Period between cell divisions - normal cell activities occurring Cell GROWS Chromosomes are copied (# doubled) Cell prepares for cell division Chromosomes chromatids. doubled becoming sister Sister Chromatid DNA (chromosomes) become visible (black squiggly lines). Nuclear membrane breaks down. Spindle Fibers appear. Spindle Fibers PULL sister chromatids to the middle of the cell. Chromosomes line up in the MIDDLE. Spindle Fibers PULL the Sister Chromatids apart. Sister Chromatids separate from their copies and move to opposite sides of the cell. Exact same chromosomes are at each end of cell Each end of cell has complete set of chromosomes Fibers disappear Nuclear membrane reforms around each set of chromosomes Cell membrane begins to pinch until cytoplasm is divided in half Two identical cells are formed One cell becomes TWO cells. Each cell has identical chromosomes. They have the same number of chromosomes as the cell they originally came from.




















![MITOSIS WORKSHEET - New Page 1 [bs079.k12.sd.us]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014668413_1-30813973b0cb9de17ced950a5cb16263-150x150.png)