* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mitosis Phases - Southington Public Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
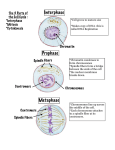
The Phases of Mitosis Interphase—this is the “In-between” phase. Chromosomes not visible for most of interphase. Chromosomes are replicated near end of interphase. Prophase—this is the “Paired” chromosome phase. Chromosomes are visible as pairs called sister chromatids. Pairs held together by centromere. Centriole and spindle fibers form in cell. Metaphase—chromosomes line up in the “Middle”. Sister chromatids line up in middle of cell and attach to the spindle fibers by the centromere. Anaphase—chromosomes move “Apart”. Centromeres split apart and chromatids separate. One chromatid from each pair moves to each side of the cell. Chromatids pull themselves apart by the spindle fibers. Telophase—“Two” cells are formed. Chromatids reach opposite sides of cell. Chromosomes unwind and become unseen again. New cell membrane (and cell wall in plants) forms between halves. Two identical daughter cells are formed.