* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2. What exists in the region around a wire that is carrying current and
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic stripe card wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic storm wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
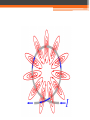
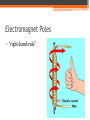
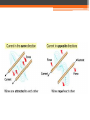
Magnetism and Electromagnets Permanent Magnet • A permanent magnet is a material that keeps its magnetic properties, even when it is not close to other magnets. Poles • All magnets have two opposite magnetic poles. Attraction Magnetic Fields • Magnetic field lines always point away from a magnet’s north pole and toward its south pole. • What does the direction of magnetic field lines tell you? • Magnetic field lines point in the direction of the force from the north pole. Magnetic Declination • The difference between the direction a compass points and the direction of true north. Gauss • The unit to measure the strength of a magnetic field. • Earth’s magnetic field averages about 0.5 gauss at the surface. Electromagnets • Magnets created by electric current flowing in wires. Earth’s Magnetism • Huge electric currents flowing in the molten iron produce the Earth’s magnetic field (like an electromagnet!). Right Hand Rule Electromagnet Poles • “right-hand-rule” Advantages • You can switch an electromagnet on and off by switching the current on and off. • You can switch an electromagnet’s north and south poles by reversing the direction of the current in the coil. • The strength can be changed by changing the amount of current in the coil. • Can be much stronger than permanent magnets when using large currents. Use right-hand-rule to describe the north and south pole. Electromagnetic Induction Magnetism in a Wire • Created by moving charges • Field lines are concentric circles with the wire at the center • Concentric: circles of different sizes Magnetic Field Strength • Directly proportional to the current, doubling the current doubles the strength of the magnetic field • Inversely proportional to the distance from the wire ▫ Stronger as you move closer to the wire ▫ Decreasing the distance to the wire by half doubles the strength of the field Coil • A single wire can be looped into a coil, concentrating the magnetic field at the coil’s center. • Solenoid Electric Motors • Convert electrical energy to mechanical energy Electric Generators and Transformers • Electromagnetic Induction – the process of using a moving magnet to create electric current or voltage. • Magnet must be moving in order to produce current • A changing magnetic field is what creates current Faraday’s Law of Induction • The voltage induced in a coil is proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic field through the coil. Sub Day Questions and Answers 2. What exists in the region around a wire that is carrying current and that exerts a force on another current-carrying wire? A magnetic field. 3. Explain how the right-hand rule can help you determine the direction of the magnetic field lines around a current-carrying wire. Wrapping the right hand around a current carrying wire with the thumb pointing in the direction of the current will cause the fingers to wrap in the direction of the magnetic field that surrounds the wire. 4. What effect does increasing the current in a wire have on the magnetic field? The magnetic field becomes stronger as the current increases. Field strength is directly proportional to the current. 5. What effect does reversing the direction of the current in a wire have on the magnetic field? The direction of the magnetic field will be reversed if the current is reversed. 6. What happens to the magnetic field as you move farther away from a currentcarrying wire? The strength of the field surrounding a wire will decrease as the distance from the wire increases. 7. Why do we not use a single wire with a large current if we wish to create a strong magnetic field? It is easier and safer to work with a small current. 10. A motor turns _____ energy into _____ energy. electrical, mechanical 11. Why is it necessary to use at least one electromagnet in a motor instead of only permanent magnets? So that the polarity of the magnets can be more easily reverses at the proper time in the rotation of the motor. 12. What is the purpose of the commutator in a motor? The commutator reverses the polarity of the electromagnets at the proper time in the sequence of rotation. 13. Why must the direction of the current in a motor’s electromagnets be switched repeatedly? The current must be continually reverses so the electromagnets will continually change polarity. 15. What happens as you move a magnet toward a coil of wire in terms of electricity? If you move a magnet through a coil of wire it will induce a potential difference in the coil that will cause a current to flow if the coil is part of a circuit. 16. If you hold a magnet still near a coil of wire, will current or voltage be induced? Explain your answer. No. A magnet will only induce a voltage in a coil if the magnet is moving relative to the coil. 17. State Faraday’s law of induction in your own words. The voltage induced across the ends of a coil is directly related to the speed with which a magnet must pass through a coil.