* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
National Electrical Code wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electrical injury wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
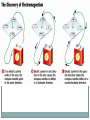
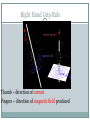
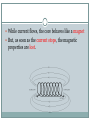
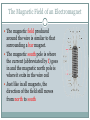
First Five Silently enter the room and sit down in your assigned seat. Begin working on your Activator. When you’ve completed your Activator, read your DEAR book. Today’s Objectives SWBAT explain identify ways to increase the strength of an electromagnet in order to describe the structure and function of an electromagnet. When electric current (moving electrons) is passed through wire, a magnetic field is formed around the wire The production of a magnetic field by electric current is called electromagnetism. Right Hand Grip Rule Thumb – direction of current Fingers – direction of magnetic field produced • A solenoid is a coil of wire that produces a magnetic field when carrying an electric current. • The electricity is what produces the magnetic field A magnet that is made by passing an electric current through a wire (in the form of a solenoid) wrapped around an iron core is called an electromagnet. While current flows, the core behaves like a magnet But, as soon as the current stops, the magnetic properties are lost. The Magnetic Field of an Electromagnet The magnetic field produced around the wire is similar to that surrounding a bar magnet. The magnetic south pole is where the current (abbreviated by I) goes in and the magnetic north pole is where it exits in the wire coil Just like in all magnets, the direction of the field still moves from north to south Ways to Increase the Strength of an Electromagnet 1) Increasing the current running through the solenoid (which can be done by increasing the voltage of the electrical source or by) A. One way to increase the voltage is to add another battery 2) Placing an iron core at the center of the coil 3) Increasing the number of coils of the wire or solenoid 4) Increasing the thickness of the wire coil Advantages of electromagnets • Turning Electromagnets On and Off Electromagnets are very useful because they can be turned on and off as needed. The solenoid has a field only when there is electric current in it. • Changing Polarity Electromagnets are also very useful to change polarity (north pole becomes south pole) Electromagnetism Anything that uses electricity or a motor most likely uses electromagnetism. Everybody Writes A magnet can be made by wrapping a _______into a coil and attaching the ends of the wire to the terminals of a battery cell. This magnet is called a(n)______________________. The strength of an electromagnet is affected by the number of ______ in the wire. The strength of an electromagnet is affected by the amount of electrical ___________ in the wire. The strength of an electromagnet is affected by the material (core) the wire is wrapped around. This core is most likely made of _________.