* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Magnets and Electricity
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
General Electric wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
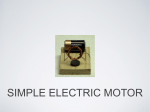
Magnets and Electricity Magnets are used to generate, or produce, electricity. Spinning a coil of wire inside a magnetic field produces an electric force between the ends of the coil. In a similar way, an electric current produces a magnetic field around it. A compass placed next to a wire carrying an electric current will point to the wire. A current-carrying wire wrapped in a coil of more wire makes a strong magnet. A coil of current-conducting wire wrapped around an iron bar makes an even stronger magnet. Around the coil is a magnetic field much like the one around a bar magnet. But a bar magnet is always magnetized, while a coil wrapped around an iron bar is a magnet only when electric current flows through the coil. For this reason it is called an electromagnet. This link between electricity and magnetism allows motion to be produced from electric energy. An electric motor uses electromagnets. By changing the direction of the electric current back and forth, these electromagnets alternately attract and repel each other. This causes the motor to turn. √ What forms around a wire carrying an electric current?