* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry in Living Things - Mercer Island School District
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
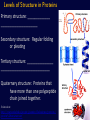
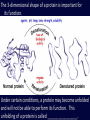
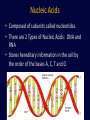
Chemistry in Living Things Organic Compounds: Molecules that are found in ______________________. Carbohydrates, Proteins, Fats, Nucleic Acids (DNA) Organic compounds contain _____________. Amino Acid (Building Block of Proteins) Discuss with your table partner: Why Carbon? Carbon is element number 6. Review what this means about its valence number and discuss how this might relate to its ability to form the complex molecules found in living things. With an atomic number of 6, carbon has ____ ___________________ . ____________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ 4 Main Types of Organic Molecules • • • • Carbohydrates Lipids (Fats and Oils) Proteins Nucleic Acids (DNA and RNA) Many organic molecules are polymers, which means they are _______________ ______________________. (poly = ____) Also called macromolecules, because they are very large. (macro = large) Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are composed of Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen in a ratio of (about) __________ Example: Glucose is C6H12O6 Most sugars and some other carbohydrates have names that end in “ ______” The sugar ribose is a 5 carbon sugar. What is its molecular formula? ______________ Types of Carbohydrates MonosaccharidesDisaccharides- simple sugars (like glucose) 2 sugars linked together Example: Sucrose = Glucose + Fructose Types of Carbohydrates Cont. Polysaccharides- polymers of many sugars Examples: Starch- _____________________________ Cellulose- _______________________________ Glycogen- _______________________________ Lipids (Fats and Oils) • Lipids are ________ in water. _________ molecules due to a large proportion of C-H bonds. • Functions of lipid include: Energy Storage Insulation Protective coating Lipids contain __________________________ as carbohydrates or proteins. Proteins Proteins are made of subunits called_________ ________. _______________________________ Amino Acids Each amino acid has a central carbon, with 4 different attachments: an amino group (NH2), a carboxyl group (COOH), a hydrogen and a side group (represented with an R). It is the side group(R) that differs among the 20 types of amino acids. The 20 Amino Acids in Proteins Protein Functions Some of the functions of proteins include: Transport proteins Example: Hemoglobin transport O2 Enzymes : proteins that catalyze a specific chemical reaction Example: Pepsin digest proteins ______________ proteins for ______________ Example: Muscle fibers _______________ proteins Example: Keratin (hair) Video: Level of Structure in a Protein http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lijQ3a8yUYQ Levels of Structure in Proteins Primary structure: _____________ _____________________ Secondary structure: Regular folding or pleating Tertiary structure: _______________ ____________________________ Quaternary structure: Proteins that have more than one polypeptide chain joined together. Animation: http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/proteins/ protein%20structure.swf The 3-dimensional shape of a protein is important for its function. Under certain conditions, a protein may become unfolded and will not be able to perform its function. This unfolding of a protein is called ________________. Nucleic Acids • Composed of subunits called nucleotides. • There are 2 Types of Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA • Stores hereditary information in the cell by the order of the bases A, C, T and G Synthesis (Building) of Polymers: Dehydration (or Condensation) Reactions Many polymers are built by reactions called dehydration (or condensation) reactions. An OH group from one subunit is linked with a H on the other subunit, _____________ . The subunits are linked covalently together. Animation of a Condensation Reaction: http://www.biotopics.co.uk/as/disacc harideformation.html Breaking down Polymers: Hydrolysis Reactions When sugars, proteins or lipids are broken down into their subunits, the opposite process occurs. Water is used in this process to break apart the polymer, so it is called a hydrolysis reaction. (hydro= _________ , lysis= ______________) Hydrolysis Reaction Animation: http://www.biotopics.c o.uk/as/disaccharidehy drolysis.html When 2 amino acids are linked together by a condensation reaction, the bond is called a peptide bond. Animation of condensation reaction for amino acids: http://www.biotopics.co.uk/as/aminocon.html Video: Carbohydrates (Observe the process of dehydration and hydrolysis reactions. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_qf_r5EVP6U Animation of condensation and hydrolysis reactions http://www.biotopics.co.uk/as/disaccharidefor mation.html http://www.tvdsb.on.ca/Westmin/science/sbioa c/biochem/condense.htm http://www.biotopics.co.uk/as/aminocon.html Discuss with your table partner: Explain the difference between carbohydrates and fats. __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ Discuss with your table partner: Why do animals store most of their excess energy as fat rather than starch? _____________________________________ _____________________________________ _____________________________________ _____________________________________