* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
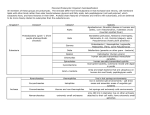
Download Cyanobacteria Eubacteria Live in: Get Energy by: Heterotrophic
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Lipopolysaccharide wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Type three secretion system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Eubacteria represents the majority of bacteria found on Earth, unlike Archaebacteria it can live in a variety of environments. Like all other bacteria they are classified as __________________ cells because they are small, simple and lack complex structures like a nucleus or organelles like a mitochondria or endoplasmic reticulum. Cyanobacteria Eubacteria Heterotrophic Eubacteria Live in: Live in: Get Energy by: Get Energy by: Archaebacteria is one of three Domains of Life which include: _____________________ and ________________________ Eubacteria are responsible for the evolution of Eukaryotes because some bacteria were ____________by other bacteria who lacked the ____________ necessary to break them down. Draw an eubacteria—include the following: Capsule, Cell Wall, Cell Membrane, Nucleoid Region, DNA, Cytoplasm and Ribosomes. Match the cellular structure with the correct function: (A) Helps bacteria attach to other bacteria/objects (B) Where cellular processes/reactions take place. (C) Creates and provide structure of cell. (D) Area where DNA is located (E) Hereditary Information (F) Makes Proteins (G) Lets nutrients and wastes in and out of cell.