* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Producing the Bovine Growth Hormone
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
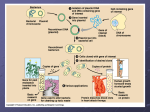
WEB TUTORIAL 15.1 Producing the Bovine Growth Hormone Text Sections Section 15.2 Transgenic Biotechnology, p. 234 Introduction How do scientists use recombinant DNA technology to produce a protein such as bovine growth hormone, which can then be used to increase milk production in cows? In this tutorial, you’ll see how bacteria can be used as factories for the production of human or other animal proteins. Learning Objectives • • Understand what a recombinant plasmid is. Know the basic steps involved in producing recombinant proteins in bacteria. Narration Cloning Genes Using Bacteria Each cell of a cow has all of the DNA needed to make all of the cow's proteins, including bovine growth hormone, or BGH. This DNA is found in the chromosomes in each cell's nucleus. To clone the BGH gene, DNA is taken from the cow cell's nucleus and cut with a restriction enzyme that leaves “sticky ends” on either side of the BGH gene. “Sticky ends” are so-named because they are able to base pair with any DNA molecule containing a complementary sticky end. The BGH gene will be cloned by putting it into a bacterial plasmid. A plasmid is a circular piece of bacterial DNA that normally exists separate from the bacterial chromosome and can replicate itself. In order to insert the BGH gene into the plasmid, the plasmid must be removed from the bacterial cell and cut open with the same restriction enzyme used on the cow DNA. When the pieces of cow DNA and the cut plasmid DNA are mixed together, their complementary sticky ends will join, forming recombinant plasmids. After the recombinant plasmid has been formed it is put back into a bacterial cell, which forms many copies, or clones, of the recombinant plasmid as it divides. Once inside the bacteria, the BGH gene can be expressed, i.e., the bacterial cell uses the information contained in the inserted BGH gene to produce BGH protein (called recombinant BGH or rBGH). The rBGH is easily separated from the bacteria and recovered from the media in which the bacteria are grown. You should now be able to… • • • Compare the experiments that Redi and Pasteur used to address the possibility of spontaneous generation and specify the experimental variables being tested in their experiments. Explain the importance of a control in an experiment. Describe the effects of boiling on microbial growth.