* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download January 23, set B
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
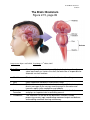
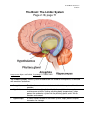
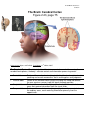
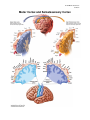
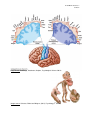
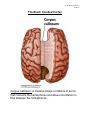
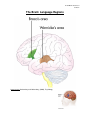
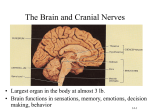
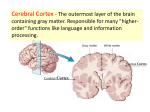
LP 3B Brain structures 1 01/06/17 The Brain: Brainstem Figure 2.15, page 69 th image source: Myers and DeWall, Psychology, 11 edition, 2015 Brain Stem The oldest part of the central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; the brainstem is responsible for automatic survival functions. • Medulla The base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing. • • Pons Thalamus • Reticular Formation Cerebellum Helps coordinate movements and controls sleep. The brain’s sensory control center, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla. A nerve network that travels through the brainstem into the thalamus and plays an important role in controlling arousal. The “little brain” at the rear of the brainstem; functions include processing sensory input, coordinating movement output and balance, and enabling nonverbal learning and memory. • LP 3B Brain structures 2 01/06/17 Medusa (image source: unknown) Medulla Medusa LP 3B Brain structures 3 01/06/17 The Cerebellum Figure 2.17, page 70 LP 3B Brain structures 4 01/06/17 The Brain: The Limbic System Page 2.18, page 71 th image source: Myers and DeWall, Psychology, 11 edition, 2015 The Limbic System: Neural system located below the cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions and drives. • Amygdala • Hypothalamus • Hippocampus Two lima-bean-sized neural clusters in the limbic system; linked to emotion. A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is link to emotion and reward. A neural center located in the limbic system; helps process explicit memories for storage. LP 3B Brain structures 5 01/06/17 The Brain: Cerebral Cortex Figure 2.23, page 75 th image source: Myers and DeWall, Psychology, 11 edition, 2015 The Cerebral Cortex: The intricate fabric of the interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres; the body’s ultimate control and information-processing center. • • • • Portion of the cerebral cortex lying just behind the forehead; involved in speaking and muscle movements and in making plans and judgments. Portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward Parietal lobes the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position. Occipital lobes Portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; includes areas that receive information from the visual fields. Temporal lobes Portions of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. Frontal lobes LP 3B Brain structures 6 01/06/17 Motor Cortex and Somatosensory Cortex LP 3B Brain structures 7 01/06/17 image source: Gazzaniga, Heatherton, Halpern, Psychological Science (2013). nd (image source: Schacter, Gilbert and Wegner, (2011), Psychology 2 edition) LP 3B Brain structures 8 01/06/17 The Brain: Cerebral Cortex Corpus Callosum: A massive bridge of millions of axons that connects the hemispheres and allows information to flow between the hemispheres. LP 3B Brain structures 9 01/06/17 The Brain: Language Regions image source: Hockenbury and Hockenbury, (2009), Psychology LP 3B Brain structures 10 01/06/17 Chapter 6: Memory Using elaborative rehearsal to remember information (page 248, 249): But if you elaborated on the information in some meaningful way, you would be more likely to recall it. For example, you could think about the limbic system’s involvement in emotions, memory, and motivation by constructing a simple story. • “I knew it was lunchtime because my hypothalamus told me I was hungry, thirsty and cold. • My hippocampus helped me remember a new restaurant that opened on campus, • but when I got there, I had to wait in line and my amygdala reacted with anger. LP 3B Brain structures 11 01/06/17 LP 3B Brain structures 12 01/06/17 Chapter 9: Motivation and Emotion The hypothalamus and regions around it play an important role in regulating eating behavior. Damage to ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH) increases eating behavior for appetizing food. Damage to the lateral hypothalamus (LH) decreases eating (and other behaviors). (image source: Hockenbury and Hockenbury, 2005, Psychology) Rat with a Damaged VMH: When a particular section of the hypothalamus, called the ventromedial hypothalamus, is destroyed, rats will eat until they become obese-—but only if the food is appetizing.