* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Notes
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
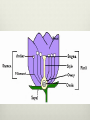
Plant Notes Kingdom Plantae Basic Characteristics Plants are: Multi-cellular Autotrophic Eukaryotic– have a nucleus Plants have: A cell wall made of cellulose that give the plant strength Chloroplasts containing chlorophyll Plants evolved from plant-like protists Nutrition Plants are Autotrophs– they make their own food. Plants use photosynthesis to convert the sun’s energy into usable energy for themselves. To do this plants use chloroplasts filled with chlorophyll. Types of Terrestrial (Land) Plants There are Two forms of terrestrial plants: 1. Non-vascular– plants have no system for transporting water or nutrients. (e.g., mosses) All non-vascular plants are seedless. 2. Vascular– plants have a system to transport water and nutrients throughout the plant. This allows the plants to be taller and live further from water. All seed plants are vascular Seedless plants (e.g., ferns) have a vascular system but reproduce using spores. Seed plants (e.g., flowers, trees) reproduce using seeds Reproduction Methods Plant reproduction can be asexual or sexual. Plants reproduce through: 1. Spores– tiny reproductive cells that can be carried long distances by the wind. 2. Seeds– a plant embryo surrounded by a protective outer coating. An embryo is made up of tissues that have the ability to grow into a new plant. Adaptations have led to several different methods of seed dispersal. ***All seed plants are vascular.*** Seed Formation & Reproduction Flowers produce pollen, which is transferred from the male anther to the female stigma during pollination. The pollen lands on the stigma and germinates, and allows sperm cells to travel to the egg in the ovary. The ovary contains ovules, each containing an egg. A sperm fertilizes the egg forming a zygote, which grows into an embryo. The ovary and surrounding structures become the fruit. Angiosperms try to avoid self-pollination by having separate male and female flowers. Types of Seed Plants Seed plants include: Gymnosperms– plants that have seeds that are not enclosed. Ex. Pines Angiosperms– flowering plants that usually have a seed enclosed in a fruit. Angiosperms are the most successful because they coevolved with insects and they use flowers and fruit for reproduction. plants Angiosperms can be arranged into two groups: 1. Monocots (e.g., grasses and palms) 2. Dicots (e.g., trees + most common plants) Leaves have parallel veins. Leaves have netlike veins. Embryos have one seed Embryos have two seed leaf. Vascular tissue in stems is scattered. leaves. Vascular tissue in stems is in arranged in a ring. Root system is fibrous. Have one main taproot. Flower parts are in Flower parts are in multiples of three multiples of four or five. Monocot Dicot