* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 22 Plant Book Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
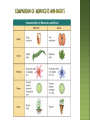
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Multicellular Eukaryotes Have cell walls made of cellulose Carry out photosynthesis using chlorophyll a &b Store energy as starch (carbohydrates) Most are autotrophs • A few are parasites (live on living organisms) or saprobes (live on dead organisms) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Sunlight Water Minerals Gas Exchange Transport of water and nutrients throughout the plant body Remember Photosynthesis: 6H2O + 6CO2 → C6H12O6 + 6O2 (water + carbon dioxide + sunlight glucose + oxygen) Plants most likely evolved from an organism like the freshwater multicelluar green algae living today. Plants had to overcome “challenges” as they moved from water to land: Adapt to be able to acquire water Adapt features to transport water Be able to conserve water more effeciently 1. Bryophytes (Mosses and their relatives) 2. Seedless Vascular (Ferns and their relatives) 3. Gymnosperms (cone-bearing plants) 4. Angiosperms (flowering plants) Water-conducting tissue (vascular) Seeds Flowers VASCULAR PLANTS – Contain tube-like cells for transport (Tracheophytes) • Can grow large and farther away from water source. NONVASCULAR PLANTS – Does not contain tube-like cells for transport. (Bryophytes) • • Water and nutrients travel by diffusion and osmosis. Small and grows close to water source • • NONVASCULAR PLANTS Plants draw up water by osmosis only a few centimeters above the ground. Low growing plants that are found in moist, shaded areas. Seedless plants – reproduce using spores RHIZOIDS – A LONG THIN CELL THAT ANCHORS MOSS TO THE GROUND AND ABSORBS H20 & MINERALS FROM SOIL Includes: Mosses Liverworts Hornworts FERNS GYMNOSPERMS (CONE BEARING PLANTS) ANGIOSPERMS (FLOWERING PLANTS) They are vascular but reproduce using spores Bear their seeds directly on the surface of cones. Vascular plants Gymnosperm means “naked seed” Includes conifers such as pines and spruces Monocots One seed leaf Parallel veins in leaves Flower parts in multiples of three’s Ex. Grass, orchids Dicots Two seed leaves Contain netted veins Flower parts in multiples of four or fives Ex’s trees, shrubs