* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure and Function
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
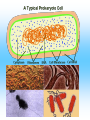
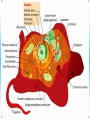
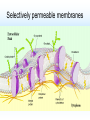
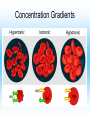
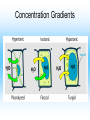
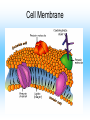
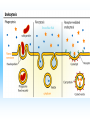
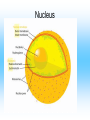
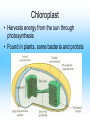
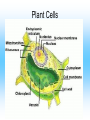
Cell Structure and Function Cells and their Functions Organelle Functions Levels of Organization • Cells can be grouped together into tissues, a group of cells that are similar and work together. – Epithelial cells epidermis Neurons nerve • Tissues can be grouped together into organs, a group of different tissues that work together to perform a specific function. – Epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous tissue skin Levels of Organization • Organs can be grouped together into organ systems, a group of organs that work together to perform specific connected tasks. – Stomach, Intestines, Liver, etc. Digestive system • Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems Major functions of cells • Break down food into nutrients – Polymers into monomers • Transport materials – O2 to cells; CO2 away from cells • Produce chemicals – Hormones – a chemical signal used to control body functions • Work together to build tissues organ systems organs organism Cell Theory • All living things are made of cells. All cells have some structures in common, such as DNA. • Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. • Cells only come from already present cells (pre-existing). Cell Types • Prokaryotes – a cell with only one outside membrane and no nucleus or other internal structures • Simple cells • Grow quickly – Binary fission, cell divides into identical daughter cells • Ex. - bacteria • Eukaryotes – a cell with several internal structures, including the nucleus, that are surrounded by membranes • Complex cells • Ex. – plant cells, animal cells, fungi cells Cell Structure and Function • Maintain homeostasis, the ability of organisms to maintain their internal conditions • Diffusion – the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration • Osmosis – the movement of water through a cell membrane • Selectively permeable membrane – a membrane that allows some molecules to pass but blocks other molecules from coming through (semipermeable) Selectively permeable membranes Concentration Gradient • A difference in the concentration of a substance across a distance is the concentration gradient. • Hypotonic – a solution whose solute concentration is lower than the solute concentration of another solution • Hypertonic – a solution whose solute concentration is higher than the solute concentration of another solution • Isotonic – a solution whose solute concentration is equal to the solute concentration of another solution Concentration Gradients Concentration Gradients Eukaryotic Cells • Contain a membrane-bound nucleus – Controls the activities of the cell • Contain membrane-bound organelles – Transports materials – Produces chemicals and substances • Complex in structure – Can reproduce in several different ways; asexual and sexual reproduction Cell Membrane • Composed of a lipid bilayer. • Hydrophilic outside, hydrophobic inside • Proteins help transport large molecules across the membrane • Glycoproteins help cells “communicate” with each other Cell Membrane Cell Membrane Function • Regulates which materials enter and leave the cell • Protects the cell from outside environment • Passive transport – the movement of molecules across a membrane when the movement requires no energy – Ex. Diffusion and osmosis • Facilitated diffusion – passive transport that involves membrane proteins Cell Membrane Function • Active Transport – the movement of molecules across a membrane when the movement requires energy • Endocytosis – a process in which a cell membrane surrounds and encloses a substance to bring the substance into the cell • Exocytosis – a process in which a substance is released from a cell through a pouch that transports the substance to the cell surface. Nucleus • Controls information in the cell • Surrounded by the nuclear envelope; bilayer contains pores to let substances enter and leave • Contains the DNA, which is folded with proteins making up the chromosomes • Nucleolus – a ball of fibers in the nucleus that makes ribosomes Nucleus Ribosomes • Make proteins from directions found in DNA • Made from a combination of RNA and other proteins • Found throughout the cell • Found on the rough endoplasmic reticulum Mitochondria • Converts energy from bonds in glucose into ATP through respiration, process in which cells break down food to release energy Chloroplast • Harvests energy from the sun through photosynthesis • Found in plants, some bacteria and protists Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) • Makes different molecules • Rough ER packages and sends off proteins • Smooth ER makes lipids and carbohydrates Golgi Apparatus • Responsible for synthesizing, modifying, and packaging proteins for export Vacuoles and Lysosomes • Vacuoles - transports and stores molecules • Lysosomes – contain special enzymes to break down large molecules • Found throughout the cell Cytoskeleton • A group of fibers running throughout the inside of a cell that supports the cell and helps the cell move • Microfilament – a long fiber used to move the cell – Made of a ball-shaped protein called actin • Intermediate filament – a rod-like fiber used to strengthen the cells shape and hold organelles in place • Microtubule – a fiber used by organelles to move around. – Made of a ball-shaped protein called tubulin Cytoskeleton Plant Cells • Plant cells contain chloroplast used in photosynthesis • Cell wall – rigid layer of cellulose outside the cell membrane • Plasmodesmata – openings in the cell wall used for communication and transport of molecules • Central vacuole – a large sac in the center of the plant cell used for water storage. Plant Cells