* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Label each of the following as homozygous or heterozygous
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
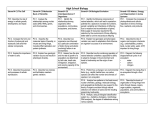
CODOMINANCE In dogs, gum coloration is co-dominant, with black coloration, black & pink spotted and pink. You have a lovely spotted gummed Labrador retriever who has just had 8 pups. Four of the pups have spotted like your dog, and 4 have black gums. 31. What is the likely phenotype of the sneaky neighbor dog? Show your work. INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE In Andalusian chickens, feather color is inherited by incomplete dominance. If one parent with black feathers (BB) is crossed with a whitefeathered parent (bb), all of the offspring will have blue feathers (Bb). 32. What is the percent chance of producing bluefeathered offspring when crossing a blue-feathered hen with a white feathered rooster? BLOOD TYPE Sometimes Blood Type alleles are written like those below: 23. Write out what the Genotype & Phenotype are for the F1 Generation DUCHENNE’S MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY This type of Muscular Dystrophy a sex linked genetic disorder that results in muscle degeneration and eventual death caused by a mutation in the dystrophin gene, the largest gene located on the human X chromosome which codes for the protein dystrophin, an important structural component within muscle tissue that provides structural stability to the dystroglycan complex (DGC) of the cell membrane. 29. Cross a carrier with a male who is normal for the dystrophin gene and give the Genotype & Phenotype for the F2 Generation. LAW OF SEGREGATION 12. State the Law of segregation. HOMOzygous vs hEtErOzygous 2. The term HOMOzygous describes ---. 3. The term hEtErOzygous describes ---. 4. Label each of the following as homozygous or heterozygous: Purple white white white MONOHYBRID CROSS Hawaiian happy face spiders from the island of Maui can have different markings, as shown below. A single gene determines the markings on the spiders. A plain spider is crossed with a patterned spider. The patterns spider is homozygous. The pattern allele is dominant to the plain allele. 5. What percentage of the offspring from this cross are expected to be patterned rather than plain? A. 0% B. 25% C. 50% D. 100% POLYGENIC INHERITANCE 16. What is polygenic inheritance? 17. Give two examples. DIBYBRID CROSS 22. If the F2 generation resulted in a 9 : 3: 3 : 1 phenotypic ratio, what would the genotype of each parent be? Use letters of your choice. SEX LINKED INHERITANCE 13. Why are males more likely to inherit a sex linked trait like Color Blindness or Hemophilia? 14. Write the genotype for a color blind male. CODOMINANCE Leaves from two white clover plants, each with a different pattern, are shown below. These flowers exhibit codominance. 15. If these two flowers were crossed, draw what the offspring would look like. KARYOTYPE 10. Is the karyotype below from a human? 11. What sex is represented on the karyotype? LAW OF INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT 28. According to Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment, what would be the expected allele combinations produced by the chromosomes below? GENETIC ENGINEERING The picture shows a process by which scientist take DNA from a human pancreas and inject it into the DNA of bacteria, thus making a new organism called Recombinant Bacteria. 30. What are these types of organisms called? DIHYBRID CROSS Fill in #8 and #9 with the correct genotypes. 8. 9. PEDIGREE CHART 25. From the above pedigree, what type of genetic disorder can you infer that it represents? 26. How many offspring did the P Generation produce? 27. Describe, using a Punnett square, how the F1 generation was determined (determine the genotypes of the parents and do a Punnett square) PEDIGREE CHART Autosomal recessive disorder 18. How many offspring did generation III, 7-8 have? 19. What do you think the line through the symbol means? 20. What person in Generation II would be homozygous dominant? 21. What person in Generation III would be homozygous dominant? DNA Structure 7. What are the subunits of DNA? Base Pairing Rules GAC-AAA-TAT-CAG 6. Given this strand of DNA, make a complementary strand. Replication 1. Write the four steps of DNA replication. BIO ETHICS 24. Why should you care about Genetically Modified plants and animals? Give an example in your answer. RNA ACG-GCA-TAA-GTA 33. Given this strand of DNA, make a complementary RNA strand. Protein Synthesis 34. Why are proteins so important? Codon Table 35. Which amino acid sequence can be coded from the DNA sequence CAG- TAG- CGA? Proteins 36. What are the building blocks (monomers) of proteins? 37. In what cell organelle are proteins made? Mutations 38. What type of mutation is caused by a change in one codon in a gene from GAA to GGA? 39. What type of mutation is show below? Normal = THE-BOY-HIT-THE-BAT Abnormal = HEB-OYH-ITT-HEB-AT Protein Synthesis 40. Fill in the order of events that leads to genetic expression? A. DNA ____ amino acid _____ traits Protein Synthesis 41. What process is X? 42. What process is Y? Protein Synthesis 43. What is the function of mRNA? 44. What is the function of tRNA? 45. What does the word synthesis mean?