* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reproduction and Genetics Vocabulary
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Life history theory wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
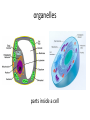
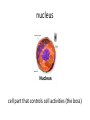
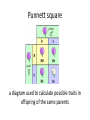
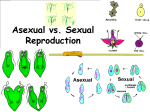
Reproduction and Genetics Vocabulary organism living thing (plant, animal, people, bacteria) reproduce to have offspring (children) of the same species sexual reproduction offspring inherit half of their DNA from each parent asexual reproduction single organism produces offspring with identical DNA to the parent pollination transfer of pollen from stamen (male part) to stigma (female part) binary fission type of asexual reproduction where organism (often bacteria) grows twice its size and splits in two, with DNA in each half bacteria conjugation bacteria shares DNA directly with a cell, using a plasmid “bridge” budding asexual reproduction where offspring develops from a bud on the parent organism spore tiny body that can grow into a new organism; often produced by plants, fungi, and bacteria fertilization joining of male and female sex cells to form a new individual development how a living thing changes during its life cell basic unit of life organelles parts inside a cell nucleus cell part that controls cell activities (the boss) cell membrane cell part that controls what enters and leaves the cell (security guard) mitosis process of cellular division resulting in two identical “daughter cells” meiosis process of cellular division resulting in four sex cells with ½ DNA genetics the study of how traits of an individual re passed on to its offspring trait a characteristic inherited from a parent or parents Examples: eye color, type of feather DNA chemical inside all cells with genetic information gene section of a chromosome that controls a specific inherited trait chromosome a structure in the cell nucleus that has DNA; each chromosome has many genes Punnett square a diagram used to calculate possible traits in offspring of the same parents dominate gene in a pair of genes, the dominate gene determines if a trait is present (B) recessive gene a gene that is masked if the dominate gene is present (b) allele each gene that codes for a different trait is called an allele pedigree a chart that shows the history of traits in a family genotype specific combination of all an organisms alleles phenotype traits an organisms exhibits (shows), based on alleles