* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIOLOGY BINGO BOARD
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
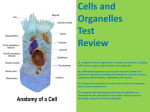
BIOLOGY BINGO BOARD FILL USE THE TERMS LISTED BELOW TO FILL IN THE BOARD ABOVE Plasma membrane Organelles Cytoplasm centrioles Nucleolus Cell respiration eukaryote Tissue Golgi Ribosomes Chloroplasts Organ systems Flagella Cell wall Osmosis Cell membrane Cell theory Passive transport mitochondria vacuole Diffusion Nuclear membrane cell Prokaryote photosynthesis Surface area to volume ratio Endoplasmic reticulum Nucleus Active transport Homeostasis Organ Cilia CELL BIOLOGY – BINGO VOCABULARY Organelles – small cell parts, each one has its own function Cytoplasm/cytosol – the clear jelly-like goop that fills up a cell, this is where chemical reactions occur in the cell, stops organelles from bumping into each other Centrioles – organelles found only in animal cells, they help move the chromosomes around during cell reproduction Nucleolus – small section of the nucleus where ribosomes are made Cellular respiration – the process which occurs inside the mitochondria, it is the chemical reaction of burning sugar to release energy, it is the opposite of photosynthesis, all living things do cellular respiration Eukaryote - a type of cell that has a nucleus and lots of different organelles, YOU have EUKARYOTIC cells Vacuole – a storage organelle, usually stores water Cell – the smallest unit of life, it is surrounded by a cell membrane, there are two types of cells: prokaryotic (bacteria) and eukaryotic (every other living thing) Flagella – a tail that hangs off of a cell to help it swim Organ systems – many different organs working together to complete one job, ex: respiratory system, skeletal system, muscular system Ribosomes – small round organelles that “read” the DNA instructions and make proteins, sites for protein synthesis Chloroplasts – organelles found in plant cells that are the sites for photosynthesis, they are green because of the pigment chlorophyll, they trap the sunlight and turn it into sugar Cell theory – three parts (a) cells are the smallest units of life (b)cells come from other cells (c) all living things have one or more cells Cell Wall – a dead, hard structure outside of a plant cell’s membrane, that helps give it support, not found in animal cells E.R. (endoplasmic reticulum) – a membrane found inside the cell that helps work like a transportation system within the cell, like a intracellular highway system Nucleus – not found in prokaryotes (bacteria), only found in eukaryotes, contains the DNA and controls ALL of the functions of the cell, surrounded by a membrane Homeostasis – maintaining a balance, ex: temperature, chemistry, water level Photosynthesis – a process that plants can do, it happens in their chloroplasts, the sunlight gets trapped and changed from light energy into food energy, Light + water + Carbon dioxide turns into Sugar + Oxygen Nuclear membrane – the envelope that surround the nucleus in a eukaryote Mitochondria – the “powerhouse of the cell”, this is where cellular respiration takes place, sugar is burned in this organelles, it acts like a furnace – burning sugar to release ATP energy Active Transport – when a cell needs to use its own energy (ATP) to move substances inside or outside, ex: white blood cells phagocytosis Prokaryote – a type of cell found ONLY in bacteria, no real nucleus, no organelles that have membranes such as: mitochondria, ER, chloroplasts Diffusion – moving substances from an area of high concentration to areas of low concentration until an equal concentration is achieved, a form of passive transport Passive transport – moving stuff to equal out concentrations, no cell energy (ATP) is spent Osmosis – moving water across a membrane to equal out concentrations, a form of passive transport Cell membrane/plasma membrane – the outer boundary of a cell, it allows some stuff in/out of cell and keeps other stuff in/out Surface area to volume ratio – cells need to stay small so that they have a high surface area to volume ratio, this lets them move stuff in and out at a rate that lets them stay alive Golgi – a group of flat sacks inside the cell that receive newly made lipids or proteins, they make the “finishing touches” and then package the products to be sent out around the cell Tissue – a group of cells all working together to do the same job, EX: many muscle cells work together as the muscle tissue to contract and move your arm Cilia – small hair-like extensions of the cell membrane, that wave back and forth and help move a cell, or help move things outside of the cell Organ – a group of tissues working together to do the same job, EX: the stomach is an organ in your digestive system that is made up of muscle tissue and lining tissue – it works to break down the food you eat into smaller parts so they can be used