* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Eukaryotic Transcription
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA-binding protein wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
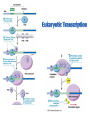
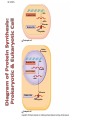
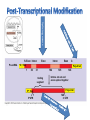
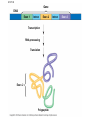
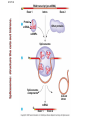
Eukaryotic Transcription • Eukaryotic Cells – cells with a nucleus and many organelles • Organisms with nucleated cells belong to the largest classification group, Domain Eukaryota • Four Kingdoms of Organisms which are eukaryotic are animal, plants, protists and fungi. Basic Principles of Transcription • Transcription is the synthesis of RNA under the direction of DNA • Transcription produces messenger RNA (mRNA) • In a eukaryotic cell, the nuclear envelope separates transcription from translation • Eukaryotic RNA transcripts are modified through RNA processing to yield finished mRNA • mRNA is a copy of the genetic code of organism. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Where is the TATAA box located? In which step does the initiation complex form? Transcription factors are associated with which structures in the diagram? Where would the codon AUG be located? Where are the genes to make a polypeptide located? Where is the termination signal located? What unwinds or melts the DNA to allow for transcription What is another name for RNA transcript? Protein Synthesis: Eukaryotic Transcription Concept 17.3: Eukaryotic cells modify RNA after transcription • Enzymes in the eukaryotic nucleus modify premRNA before the genetic messages are dispatched to the cytoplasm • During RNA processing, both ends of the primary transcript are usually altered • Also, usually some interior parts of the molecule are cut out, and the other parts spliced together • Exon – coding region and Intron –noncoding region Make a table like the one below in your notebook. As you watch the video, complete it with information. Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Transcription Characteristic Nucleus present Uses a specific type of RNA polymerase Have Ribosomes Location of Transcription DNA contains exons DNA contains introns Modifies mRNA Location Translation Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell LE 17-3-5 DNA TRANSCRIPTION mRNA Ribosome TRANSLATION Polypeptide Prokaryotic cell Nuclear envelope DNA TRANSCRIPTION Pre-mRNA RNA PROCESSING mRNA Ribosome TRANSLATION Polypeptide Eukaryotic cell Prokayotic versus Eukaryotic Proteins Synthesis • Smaller cell size • No nucleus – nucleoid region for DNA • Ribosome only organelle • Smaller size chromosome • Circular chromosome • Chromosome contains only coding regions for proteins • Larger cell size • Nucleus contains DNA and a nucleolus for RNA • Ribosome and other organelles • Larger size chromosome • Linear chromosome • Chromosome contains coding and noncoding regions for proteins Splicing exons 5 Exon Intron Pre-mRNA 5 Exon Intron Exon 3 Cap Poly-A tail 1 30 31 Coding segment 5 104 105 146 Introns cut out and exons spliced together Poly-A tail Cap 5 UTR 1 146 3 UTR Alteration of mRNA Ends in Eukaryotic Cells • Each end of a pre-mRNA molecule is modified in a particular way: – The 5 end receives a modified nucleotide cap – The 3 end gets a poly-A tail • These modifications share several functions: – They seem to facilitate the export of mRNA – They protect mRNA from hydrolytic enzymes – They help ribosomes attach to the 5’ end LE 17-12 Gene DNA Exon 1 Intron Exon 2 Transcription RNA processing Translation Exon 2 Polypeptide Intron Exon 3 LE 17-11 RNA transcript (pre-mRNA) 5 Exon 1 Intron Exon 2 Protein Other proteins snRNA snRNPs Spliceosome 5 Spliceosome components Cut-out intron mRNA 5 Exon 1 Exon 2 • In some cases, RNA splicing is carried out by spliceosomes • Spliceosomes consist of a variety of proteins and several small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) that recognize the splice sites • RNA splicing can lead to genetic diversity Helpful Transcription Animation Links • • • • Stages of Transcription: Components Transcription Factors RNA Splicing and Spliceosome RNA Splicing