* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
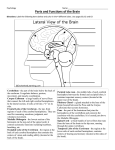
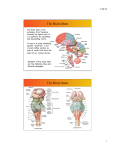
STUDY GUIDE #4 – THE BRAIN – pp. 215 - 221 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. What is the first appearance of the CNS in a developing embryo? What happens to this structure by the fourth week of development? What does the remainder of this structure become? What are the four chambers of the brain called? How much does the adult brain weigh? What are the four major regions of the brain? Which part of the brain is the largest and most superior? What are gyri? What are sulci? How are fissures different from sulci? How are the lobes of the brain named? List the seven functions of the cerebral cortex neurons. Look in the right column on this same page and tell what the cerebral cortex is. What is the nature of this area of the brain? What is the significance of this arrangement? What does the somatic sensory area allow you to do? Which side of the sensory cortex receives impulses from the right side of the body? Tell what is interpreted in each of these areas: parietal lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe. What part of the brain allows us to consciously move our skeletal muscles? Where is this area? What is controlled in the Broca’s area? Which hemisphere is this usually in? What happens when there is damage to the Broca’s area? Where are areas of higher intellectual reasoning located? Where are complex memories stored? Where is the speech area? What does it allow you to do? What area controls language comprehension? What function does the white matter of the cerebral hemispheres have? What is the corpus callosum? What is it responsible for? Why is the function of the corpus callosum important? What are basal nuclei? What is affected by problem here? List two diseases that affect the basal nuclei. Where is the diencephalon? List the three structures of the diencephalon. What is the function of the thalamus? As impulses move through this area, of what are we aware? How do we then interpret this information? What three important functions does the hypothalamus have? List the five limbic centers found in the hypothalamus. What gland does the hypothalamus regulate? What is the purpose of the mammillary bodies? What system is the pineal body, found in the epithalamus part of? How long is the brain stem? List the three parts of the brain stem. Name two vital activities controlled by the brain stem. What function is carried out by the corpura quadrigeminia? In what part of the brain stem are they located? STUDY GUIDE #4 – THE BRAIN – pp. 215 - 221 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. What is the first appearance of the CNS in a developing embryo? What happens to this structure by the fourth week of development? What does the remainder of this structure become? What are the four chambers of the brain called? How much does the adult brain weigh? What are the four major regions of the brain? Which part of the brain is the largest and most superior? What are gyri? What are sulci? How are fissures different from sulci? How are the lobes of the brain named? List the seven functions of the cerebral cortex neurons. Look in the right column on this same page and tell what the cerebral cortex is. What is the nature of this area of the brain? What is the significance of this arrangement? What does the somatic sensory area allow you to do? Which side of the sensory cortex receives impulses from the right side of the body? Tell what is interpreted in each of these areas: parietal lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe. What part of the brain allows us to consciously move our skeletal muscles? Where is this area? What is controlled in the Broca’s area? Which hemisphere is this usually in? What happens when there is damage to the Broca’s area? Where are areas of higher intellectual reasoning located? Where are complex memories stored? Where is the speech area? What does it allow you to do? What area controls language comprehension? What function does the white matter of the cerebral hemispheres have? What is the corpus callosum? What is it responsible for? Why is the function of the corpus callosum important? What are basal nuclei? What is affected by problem here? List two diseases that affect the basal nuclei. Where is the diencephalon? List the three structures of the diencephalon. What is the function of the thalamus? As impulses move through this area, of what are we aware? How do we then interpret this information? What three important functions does the hypothalamus have? List the five limbic centers found in the hypothalamus. What gland does the hypothalamus regulate? What is the purpose of the mammillary bodies? What system is the pineal body, found in the epithalamus part of? How long is the brain stem? List the three parts of the brain stem. Name two vital activities controlled by the brain stem. What function is carried out by the corpura quadrigeminia? In what part of the brain stem are they located? 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. What function is controlled in the pons? Where is the medulla oblongata? What does the medulla oblongata merge with? List five functions controlled by the medulla oblongata. What is the RAS? What happens if it is damaged? Where is the cerebellum? What are the two major functions of the cerebellum? What is the nature of our body movements because of its activity? To what can the cerebellum be compared? Why? What happens to movement if the cerebellum becomes damaged? What is this called? Give an example of a normal action that cannot be accomplished if the cerebellum is damaged. Name the three materials that enclose the nervous tissue to protect it. What protects nervous tissue from harmful substances in the blood? What are meninges? Name the three meninges. Distinguish between each of the type of meninges in terms of location and appearance or nature. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. What function is controlled in the pons? Where is the medulla oblongata? What does the medulla oblongata merge with? List five functions controlled by the medulla oblongata. What is the RAS? What happens if it is damaged? Where is the cerebellum? What are the two major functions of the cerebellum? What is the nature of our body movements because of its activity? To what can the cerebellum be compared? Why? What happens to movement if the cerebellum becomes damaged? What is this called? Give an example of a normal action that cannot be accomplished if the cerebellum is damaged. Name the three materials that enclose the nervous tissue to protect it. What protects nervous tissue from harmful substances in the blood? What are meninges? Name the three meninges. Distinguish between each of the type of meninges in terms of location and appearance or nature.