* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
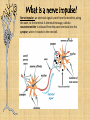
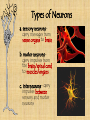
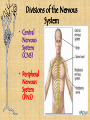
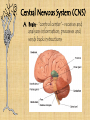
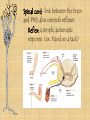
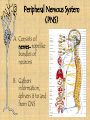
3/5 • Get out Body Systems Booklet – Open to nervous system lab – Go back to your trials and continue your analysis questions REGULATION Nervous System -Regulation requires homeostasis –the ability of the body or a cell to seek and maintain stability within its internal environment when dealing with external changes. -The nervous system maintains homeostasis by controlling and regulating all other parts of the body. Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory-uses receptors to gather information from all over the body 2. Interpretation-the brain then processes the information into possible responses 3. Response-sends messages back through the system of nerve cells to control body parts Evolutionary Trends of the Nervous System Complex Simple Animal Taxon Type of Nervous Tissue Aquatic Invertebrates Flatworms & Roundworms Segmented Worms & Arthropods Vertebrates A simple system with interconnected neurons called nerve nets; contain specialized cells for touch and chemical detection Ganglia (a group of nerve cells) and nerve cords run along the body; can detect chemicals, touch, and some have eyespots Cephalization occurs which is the concentration of nerve cells in a head region to form a brain; intense senses in arthropods A well developed brain evolved from the spinal cord; the size and complexity increases from fish to mammals Picture of system planaria, flukes, Examples jellyfish tapeworm, hookworm earthworm, ants, grasshopper, bees mammals, birds, reptiles, fish, amphibians Structures of the Nervous System Neurons: the functional cell that transmits signals through the body; an individual nerve cell Parts of a Neuron 1. cell body- the largest part of the neuron; contains the nucleus and organelles 2. dendrites- short, branching extensions spreading out from the cell body; receive and carry impulses to the cell body 3. axon- long, fibrous part of neuron; conducts nerve impulses away from cell body 4. at the end of the axon, the impulse travels across the synapse, a tiny gap separating the axon of one neuron from the dendrite of another What is a nerve impulse? Nerve Impulse- an electrical signal is sent from the dendrite, along the axon, to the terminal. A chemical message, called a neurotransmitter is released from the axon terminals into the synapse, where it travels to the next cell. Types of Neurons a. sensory neuronscarry messages from sense organs to brain b. motor neuronscarry impulses from the brain/spinal cord to muscles/organs c. interneurons- carry impulses between sensory and motor neurons Divisions of the Nervous System • Central Nervous System (CNS) • Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Central Nervous System (CNS) A. Brain- “control center”- receives and analyzes information; processes and sends back instructions Parts of the Brain 1. Cerebrum controls thought, language, learning, judgment, & voluntary action 2. Cerebellum controls involuntary functions of muscles & maintains balance and posture 3. Brain stem Controls involuntary functions such as breathing, heart rate, and swallowing 4. Thalamus, Hypothalamus Controls homeostasis- temperature, hunger, thirst, fight or flight responses Spinal cord- link between the brain and PNS; also controls reflexes Reflex: a simple, automatic response (ex. Hand on a tack) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) A. Consists of nerves- ropelike bundles of neurons B. Gathers information, delivers it to and from CNS Levels of Organization Neurons Nerves Brain Nervous Interaction with other systems for Regulation Bones of the skeletal system protect the spinal cord and brain. The brain controls heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing via the circulatory and respiratory systems. Glands in the brain control the release of hormones of the endocrine and reproductive systems. The brain controls muscles both in digestion and movement. Diseases / Disorders of the Nervous System 1. Polio- a virus that attacks the spinal cord; eventually causes paralysis 2. Multiple Sclerosis (MS)- affects neurons; slows nerve impulses, causing muscle weakness, possibly paralysis. 3. Alzheimer’s- brain tissue deteriorates; severe memory loss 4. Stroke- a blockage in a blood vessel in the brain, causing brain damage 5. Concussion- a bruise to the brain when the brain hits the inside of the skull Fun Facts A human body contains more nerve cells than there are stars in the Milky Way Neurons are the largest cell in the body and do NOT undergo mitosis Nerve impulses move at 100 meters per second or more Longest axon of a neuron is 15 ft! (in the giraffe) 3/5 • Get out your nervous system notes packet • Pick up the “Touch Receptor Lab” • Get out a spare sheet of paper for your warm-up (1st & 2nd period only) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Warm-Up Most athletes have impeccable coordination and balance. What part of the brain controls these functions? After a serious car accident, a man suffers a traumatic head injury. The man is still breathing and his heart is functioning but he is in a coma. What part of his brain is still intact? A student thinks it’s a good idea to jump off of a roof into a neighbor’s pool below…what part of his brain is responsible for his LACK of judgment and thought? You are jogging at night and a large dog starts to chase you!! What part of your brain will release the hormone “adrenaline” to allow you to fight or escape the animal? List in order the direction an electrical impulse travels down a neuron: