* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Conclusions Synapsin IIa is expressed in the brain of adult zebrafish
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of depression wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
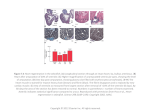
(Cesca et al. 2010) The Identification and Expression of Synapsin IIa in Zebrafish Kelly Welsh and Wendy Boehmler, Department of Biological Sciences York College of Pennsylvania addiction-dirkh.blogspot.com Introduction ZF 2a •Synapsins (I, II, and III) are a family of neuronal phoshoproteins that play an important role in neurotransmitter release by releasing synaptic vesicles in the presynaptic terminal to move towards the plasma membrane for exocytosis. Human2b2 ZF 2a ZF 2a ZF 2a ZF 2a PCR Purification of Synapsin IIa Transformation Ligation Used tissues from zebrafish brain, eye, gut, heart & muscle and 24, 42, and 72 hours post fertilization (hpf) embryos 289 Human2b302 ZF 2a Results 349 Human2b362 ZF 2a 408 Ladder Ladder Human2b422 2. Determine if there is expression of synapsin IIa gene during different developmental timepoints in zebrafish embryos. •RT-PCR was conducted using RNA collected from adult zebrafish and embryos. 229 Human2b242 ZF 2a 1. Determine if there is expression of the synapsin IIa gene in adult zebrafish tissues. •Searches of expressed sequence tag databases (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) led to the identification of a potential zebrafish Synapsin IIa homolog (Gene Accession number NM001002597). 169 Human2b182 •Because zebrafish are now being increasingly used as a genetic model and to model a variety of human diseases, we focused our studies on the cloning and characterization of zebrafish synapsin IIa. Methods 109 Human2b122 •Synapsins and synapsin-like genes have been characterized in a variety of invertebrates and vertebrates, however the synapsin genes have yet to be characterized in zebrafish. Objectives 59 Human2b62 •Synapsins have also been implicated in neurite outgrowth, the stabilization of synapses, and synaptic vesicle docking, fusion, and recycling. •It has been reported that synapsin II expression levels are decreased in post-mortem brain samples of schizophrenic patients. It is unclear whether the decrease in expression is the cause or result of the disease or whether antipsychotic drug treatment effects the expression of synapsin II. 1 MNYLRRRLSDSTFISNLPNGYMSDLQKPDPPQPPPPGPAPVPAPASGPAPVSPRQ--ERK MN+LRRRLSDS+FI+NLPNGYM+DLQ+P+P QPPPP P A ++ AP + ER+ MNFLRRRLSDSSFIANLPNGYMTDLQRPEPQQPPPPPPPGPGAASASAAPPTASPGPERR PIQPQP---------GLGTGFFSSITNVVKQTAASAGLVEQTSVPASSKR-IKILLVIDE P +G+ FFSS++ VKQTAASAGLV+ + ++ R K+LLV+DE PPPASAPAPQPAPTPSVGSSFFSSLSQAVKQTAASAGLVDAPAPAPAAARKAKVLLVVDE 58 61 108 121 PQHDWAKLFRGKKLNGDYDIKVEQAEFGDISIVAHANGSCNVAVQVLQNENKVLRSFKPD P DWAK FRGKK+ GDYDIKVEQAEF ++++VAHA+G+ V +QVL+N KV+RSF+PD PHADWAKCFRGKKVLGDYDIKVEQAEFSELNLVAHADGTYAVDMQVLRNGTKVVRSFRPD 168 FVLIRQHAFSMTENEDFRNLIIGLQYAGIPSINSLESVYNLCDKPWAFACLINTYKKLGQ FVLIRQHAF M ENEDFR+LIIG+QYAG+PSINSLES+YN CDKPW FA L+ YK LG FVLIRQHAFGMAENEDFRHLIIGMQYAGLPSINSLESIYNFCDKPWVFAQLVAIYKTLGG 228 EKFPLIEQTFYPNYKEMVTMPAFPVVVKIGHAHSGVGKVKVENHTKFQDIASVVAITQTY EKFPLIEQT+YPN+KEM+T+P FPVVVKIGHAHSG+GKVKVENH FQDIASVVA+TQTY EKFPLIEQTYYPNHKEMLTLPTFPVVVKIGHAHSGMGKVKVENHYDFQDIASVVALTQTY 288 STCEPFIDPKYDIRIQKIGNDYKAYMRTSVSGNWKSNTGTAMVEQVAMTDRYKLWVDTCC +T EPFID KYDIR+QKIGN+YKAYMRTS+SGNWK+NTG+AM+EQ+AM+DRYKLWVDTC ATAEPFIDSKYDIRVQKIGNNYKAYMRTSISGNWKTNTGSAMLEQIAMSDRYKLWVDTCS 348 EIFGGLEICAVKAINGKDGKDYITEVMGSSMPLMGEHQAQDQQLIADMVIAKMNHVMAQE+FGGL+ICAVKA++GKDGKDYI EVM SMPL+GEHQ +D+QLI ++VI+KMN ++++ EMFGGLDICAVKAVHGKDGKDYIFEVMDCSMPLIGEHQVEDRQLITELVISKMNQLLSRT 407 ---NPKRP-TAIQPKQITVENNTLVEVKNAPPQKAPPQGCLQYILDCNGVAVGPKLVQAN +P+RP T QP+ T+++ + PPQ+ PPQGCLQYILDCNG+AVGPK VQA+ PALSPQRPLTTQQPQSGTLKDP---DSSKTPPQRPPPQGCLQYILDCNGIAVGPKQVQAS 181 241 301 361 421 463 478 Figure 4: Comparison of zebrafish and human Synapsin II. Human and zebrafish SynapsinII amino acid sequences were aligned using CLUSTALW. Dashes in sequences allow optimal alignment for amino acid insertions/deletions. Identical amino acids are shown and similar amino acids are highlighted by plus signs. (Identities = 314/480 (66%) ) Domains A and C are highlighted, Domain A and B contain phosphorylation sites and Domain C stabilizes the interaction. Table 1: Markers and Genes Syntenic with SynII Gene in Zebrafish and Humans. Figure 1: RT-PCR analysis of Synapsin IIa from zebrafish embryos. The SynIIa gene was amplified from zebrafish brain, 24 hpf, and 72 hpf. The primers used encompassed the predicted ATG start codon and stop codon to produce an amplicon of 1420 base pairs (bp). Zebrafish Human Gene Name Chromosome Chromosome SynII rhoa craf plxnbl tkt her9 slc41a3 23 23 23 23 23 23 23 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Conclusions RNA Isolation 1. Synapsin IIa is expressed in the brain of adult zebrafish, however we did not find expression in the eye, gut, muscle, or heart. 2. The data presented here represents the first analysis of temporal expression of the synapsin IIa gene in developing zebrafish embryos. PCR Denatured at 95°C Annealed at 46°C Elongated at 72°C cDNA 3. Sequence comparisons and syntenic analysis supports the identification of a novel zebrafish synapsin II homolog. Future Experiments 30 cycles • Determine the spatial expression of synapsin IIa gene during different developmental timepoints in zebrafish embryos • Perform a whole-mount in situ hybridization on embryonic zebrafish using the cloned synapsin IIa gene to determine its spatial and temporal expression pattern. • Determine whether antipsychotic drug treatment alters the expression levels of synapsin IIa in zebrafish. Zebrafish Synapsin IIa gene cloned Literature Cited •Cesca, F., Baldell, P., Valtorta, F., & Benefenat, F. (2010). The synapsin key actors of synapse function and plasticity. Progress in Neurobiology, 91, 313-348. •Chong, V.Z., Skoblenick, K., Morin, F., Xu, Y., Mishra, R.K., 2006. Dopamine-D1 and -D2 receptors differentially regulate synapsin II expression in the rat brain. Neuroscience, 138, 587–599.