* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download APCh43ImmunityDiagrams_Terms
Survey
Document related concepts
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
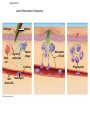
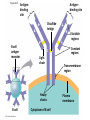
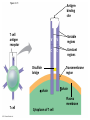
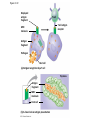
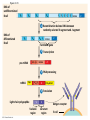
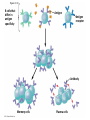
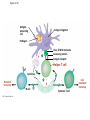
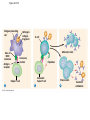
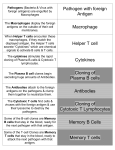
Diagrams & Terms Chapter 43 Match the Terms 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. General term: engulfs, traps & digests invader Protein that a virus-infected cell secretes, inducing nearby cells to inhibit viral reproduction Protein that tags antigens for destruction Type of WBC, originates from stem cells in bone marrow, general term Circulate in blood, are attracted by signals, engulf & destroy pathogens Lymphocytes that mature & remain in blood, release chemicals to destroy abnormal cells Found beneath mucousal surfaces, defend against multicellular invaders using destructive enzymes. Lymphocytes for viruses inside host cells Populate tissues that contact the environment, stimulate adaptive immunity Proteins circulate through blood in an inactive state, activated by surfaces of microbes, begins reactions that lead to lysis of microbe Lymphocytes that mature in the bone marrow Any foreign substance that stimulates an immune response Large eaters, migrate through body or remain permanently in certain tissues/organs A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. Eosinophils Antigen B cells Antibody Lymphocytes Complement System Natural killer cells T cells Neutrophils Dendritic cells Macrophages Phagocytic cell Interferons Figure 43.8-3 Local Inflammatory Response Pathogen Mast cell Splinter Macrophage Signaling molecules Capillary Neutrophil Red blood cells Movement of fluid Phagocytosis Figure 43.9 Antigenbinding site Antigenbinding site Disulfide bridge Variable regions B cell antigen receptor C Light chain Heavy chains B cell Cytoplasm of B cell C Constant regions Transmembrane region Plasma membrane Figure 43.11 Antigenbinding site T cell antigen receptor V V Variable regions C C Constant regions Disulfide bridge chain T cell Transmembrane region chain Plasma membrane Cytoplasm of T cell Figure 43.12 Displayed antigen fragment T cell T cell antigen receptor MHC molecule Antigen fragment Pathogen Host cell (a) Antigen recognition by a T cell Top view Antigen fragment MHC molecule Host cell (b) A closer look at antigen presentation Figure 43.13 DNA of undifferentiated B cell V37 V39 V38 V40 J1 J2 J4 J3 J5 C Intron 1 Recombination deletes DNA between randomly selected V segment and J segment DNA of differentiated B cell V37 V39 J5 V38 C Intron Functional gene 2 Transcription V39 J5 pre-mRNA Intron C 3 RNA processing mRNA Cap V39 J5 C Poly-A tail V V V V 4 Translation C C Light-chain polypeptide V Variable region C Constant region C Antigen receptor B cell C Figure 43.14 B cells that differ in antigen specificity Antigen Antigen receptor Antibody Memory cells Plasma cells Figure 43.15 Primary immune response to antigen A produces antibodies to A. Secondary immune response to antigen A produces antibodies to A; primary immune response to antigen B produces antibodies to B. Antibody concentration (arbitrary units) 104 103 Antibodies to A 102 Antibodies to B 101 100 0 7 Exposure to antigen A 14 21 28 35 Exposure to antigens A and B Time (days) 42 49 56 Figure 43.16 Antigenpresenting cell Antigen fragment Pathogen Class II MHC molecule Accessory protein Antigen receptor 1 Helper T cell Cytokines Humoral immunity B cell 3 2 Cytotoxic T cell Cellmediated immunity Figure 43.17-3 Cytotoxic T cell Accessory protein Class I MHC molecule Infected cell 1 Released cytotoxic T cell Antigen receptor Perforin Pore Antigen fragment 2 Dying infected cell Granzymes 3 Figure 43.18-3 Antigen-presenting cell Class II MHC molecule Antigen receptor Pathogen Antigen fragment B cell Accessory protein Cytokines Activated helper T cell Helper T cell 1 Memory B cells 2 Plasma cells 3 Secreted antibodies Figure 43.22 Histamine IgE Allergen Granule Mast cell Figure 43.23 Helper T cell concentration (in blood (cells/mm3) Figure 43.25 Latency AIDS Relative anti-HIV antibody concentration 800 Relative HIV concentration 600 Helper T cell concentration 400 200 0 0 1 3 7 2 4 5 6 Years after untreated infection 8 9 10 Figure 43.26