* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure of the Nervous System
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Perivascular space wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Cerebral cortex wikipedia , lookup
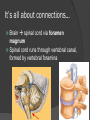
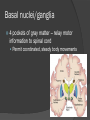
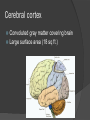
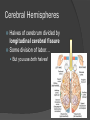
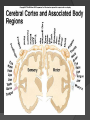
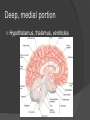
Revisit Plasticity: Phineas Gage At the center of everything… but separated by layers of membranes It’s all about connections… Brain spinal cord via foramen magnum Spinal cord runs through vertebral canal, formed by vertebral foramina Meninges mater (umm… matter) Dura mater – “durable” tough, dense; protection from impact, friction Arachnoid mater – cushion from impact Subarachnoid space – CSF runs here Pia mater – in the “pits” direct contact Carries blood vessels Forms nerve sheaths Helps form CSF More on the pia mater Associated with choroid plexus Secretes CSF Combination of blood vessels & neuroglia ○ Remember which kind? Ependymal cells It’s not all black and white… but it is gray! Gray matter = unmyelinated neuron cell bodies Accumulate lipofuscin Found primarily in cortex (surface of brain) ○ Highly folded/ridged = gyri Increase surface area Small pockets of gray found in interior White matter = myelinated axons, neuroglia Found in brain’s interior In spinal cord, colors are reversed… outside white, inside gray Concept check! 1. Describe the three layers of the meninges 2. What is the function of the choroid plexus? 3. Describe the locations of gray and white matter in the CNS Why are they those colors? Three-Pound Marvel: The Brain Billions of neurons, neuroglia Most multipolar (1 axon, many dendrites) Receive many signals, process them Tracts of axons Information conduit other regions of brain, body Forebrain: Cerebrum and diencephalon Largest, most anterior portion Emotions Memory Motor movement Thought Contain basal nuclei, cerebral cortex Basal nuclei/ganglia 4 pockets of gray matter – relay motor information to spinal cord Permit coordinated, steady body movements Cerebral cortex Convoluted gray matter covering brain Large surface area (18 sq ft.) Blood-brain barrier Cerebral cortex nourished by vessels in arachnoid layer “Barrier” exists between bloodstream and CSF… Which neuroglia create this? Astrocytes! Prevents harmful substances from entering brain (also medications) Cerebral Hemispheres Halves of cerebrum divided by longitudinal cerebral fissure Some division of labor… But you use both halves! Communication between hemispheres Corpus callosum connects left and right hemispheres Contributes to plasticity of brain Four lobes of the cerebrum Central sulcus Lateral sulcus Areas of specialization Deep, medial portion Hypothalamus, thalamus, ventricles