* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RNA Ligands to Bacteriophage T4 DNA Polymerase
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Cooperative binding wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
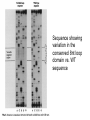
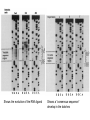
Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment: RNA Ligands to Bacteriophage T4 DNA Polymerase CRAIG TUERK AND LARRY GOLD So what was being studied? • The interaction of bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase (gp43) and the ribosome binding site of the mRNA that it encodes But a bit of background first… • Binding gp43 overlapping the SD sequences prevents translation and promotes autogenous regulation • The minimum target size of the RNA is 36nt which includes a 5bp helix and 8nt loop This is also conserved in phage RB69 To investigate what is responsible for this loop bias, the researches created the SELEX method to select preferred binding sequences from a random sequence pool But what the heck is SELEX? • Sytematic Evolution of Ligands by EXponential enrichment. • The method relies on mechanisms that are often ascribed to evolution to accomplish its goal. – Variation – Selction – Replication Variation Selection Replication Creation of Variant Sequences • Created a 110nt ssDNA transcript by ligating three oligonucleotides together and two bridging oligos • Oligo 4 was randomized for the 8nt of the loop sequence (AAUAACUC), creating 65,536 sequences • WT sequence was also engineered and used for comparison with the results. Sequence showing variation in the conserved 8nt loop domain vs. WT sequence Comparison of dissociation constants • Kd for WT:gp43 = 5x10^-9 • Kd for variant sequences = 3.2x10^-7 – WT binding is about 60x stronger than variant sequences, but only 100x stronger than nonspecific binding So this leads us to a goal • To enrich for the highest affinity RNA ligands to gp43 Experiment • Three experiments were carried out at different concentrations ratios of RNA to gp43. • A=10 • B=1000 • C=100 • RNA was added to gp43 in excess of binding sites so that competitive binding occurred. • Amount of RNA retrieved was roughly equal to the amount of gp43 in the reaction Selection was carried out by allowing gp43 to bind RNA ligand. Complex was purified by capture in a nitrocellulose filter. -Purified RNA was subjected to reverse transcriptase and PCR amplification -Amplified cDNA was converted to RNA with T7 transcription What happened? • After four rounds of selection the labeled products exhibited binding that was indistinguishable from WT binding – Though it is not explained HOW they know this • Three rounds of B were gel purified and sequenced • The final round of all the experiments were purified and sequenced. Shows the evolution of the RNA ligand Shows a “consensus sequence” develop in the batches • WT sequence is present in the consensus sequence • Using quantification data, it is shown there is a slight bias for the WT (data not shown) So what sequences are represented? • Individual sequences from B were cloned into pUC18 (plasmid). Bam H1 and Hind III sequences were added for entry. • 20 individual clones were selected and sequenced 2 predominant sequences found • WT AAUAACUC was found nine times • AGCAACCU was found eight times – Will now be referred to as Major Variant, MV • 3 other single transition mutants were found Additional binding experiment • Sequences were excised from plasmid and filtered as before on nitrocellulose. There is a correlation between selected abundance and binding affinity. Another additional binding experiment • Additional experimenting (not shown) determined that WT and MV compete for gp43 and that the dissociation constant for WT is twice that of MV. Paradox? • The loop of eight nucleotides is conserved, even to the distant phage RB69, yet the change in dissociation constant it brings only represents a minimal change in binding energy (2.5 kcal). • Other mutations around this region can provide a higher binding energy, but are not as well conserved. Models for RNA sequence equivalence. • Bound WT may contain an AC pair in its loop • Extra base pair in MV may be denatured by binding • Each form may make equivalent but not identical contacts with protein • Each loop sequence may participate in unusual base pair combinations with the operator folding the RNA. This would require further structural study Evolution • As stated before, SELEX uses mechanisms associated with evolution, and can be thought of as in vitro evolution. – Binding is a selective pressure – A vast number of variant RNA are sampled at once and selected out – Replication is carried out by PCR and T7 RNA polymerase Evolution of Ligand • The authors predict that since the operatorrepressor relationship exists, that it must have conferred at some time a selective advantage • Other regions must have been under more functional constraint. Location of the operator did not infringe on coding regions or other operator sequences • T4 sequences tend to be AT rich, so operators should be biased to be AU rich. • Despite the constraints of experimental design SELEX came up with the same answer as natural evolution did. So SELEX is pretty cool, isn’t it? • The authors sure seem to think so SELEX is a technique that combines genetic selection and precision from biochemical technique. It is somewhat simple to use in that there needs to be no other scorable phenotype than binding to partitioning agent. Application of SELEX • Can be used to determine optimal binding sequences for any nucleic acid binding protein • Study interactions between TFs, repressors and binding sequences • Develop RNA molecules to interact with other substrates giving examples of how the “RNA world” may have functioned – Could be a step toward replicating some of those early enzymes • Nucleic acid ligands as specific inhibitors of proteins • Evolution in a test tube