* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EVOLUTION study guide File
Survey
Document related concepts
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Sympatric speciation wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
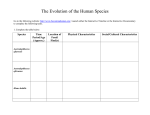
Unit 5 Evolution Study Guide Know the definitions to the following vocabulary words: Overproduction Struggle for existence Fitness Adaptation Natural Variation Inheritance Difference in Reproductive success Survival of the Fittest Natural Selection Descent with modification Homologous structures Vestigial Organs Artificial selection Reproductive Isolation Speciation Geographic isolation Temporal isolation Behavioral isolation DNA Genetic mutation Evolutionary tree Common ancestor Bipedalism Homo erectus Homo neanderthalensis Australopithecus afarensis Homo sapien Hominid Address the learning objectives below Lamarck’s Evolution Hypothesis o According to Lamarck, how did organisms acquire traits. o Describe the differences and similarities between Darwin’s ideas of evolution and Lamarck’s ideas about evolution ((hint consider Lamarck’s ideas of Acquired characteristics, and Darwin’s idea of decent with modification) Summarize Darwin’s ideas on evolution o Define what is meant by the word “natural variation” o Describe how common genetic variation is in populations of plants and animals o Explain how evolution is defined in genetic terms o Identify two main sources of genetic variation: o Explain why some individuals survive and others do not o Explain what is meant by “survival of the fittest” o Explain the roll inheritance and genetics have in evolution Common Decent o Analyze Evolutionary Trees and predict evolutionary relationships (common ancestors) Evidence o Explain how the Fossils Record provides evidence for the theory of evolution o Define and give an example of a Vestigal Structure o Define and give an example of a Homologous Structure o Explain how DNA evidence support Darwin’s ideas about evolution o Similarities in Embryology o Artificial Selection Process of Speciation o Identify an important factor that is necessary for the formation of a new species o Identify ways that populations of the same species can become reproductively isolated. o Explain why geographic isolation of two populations of a species tends to increase differences between their gene pools. o Identify all the steps which occurred in the speciation of the Galápagos finches o Explain why the Galapagos finches are an excellent example of speciation. o Describe what forces drive the speciation in Galapagos’ Finches Coevolution o Define Co-evolution and give an example of two species that probably co-evolved Human Evolution (becoming human video clip notes) o Identify some characteristics modern humans share with primates o Know where the first Hominids evolved o Describe how hominids differed from the apes o Know the famous fossil “Lucy” was the species Australopithecus afarensis o Explain what is meant by the statement, “ chimpanzees are our closest living relative” o Know that there were several Homo species that exist before and with Homo sapiens, and be able to identify Homo neaderthalensis, Homo erectus and Homo hablis.