* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemical Reactions - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
Catalytic reforming wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Fluorochemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Properties of water wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
Franck–Condon principle wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Fine chemical wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Supramolecular catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical biology wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Host–guest chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen bond wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Computational chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Self-assembled monolayer wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Abiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular scale electronics wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
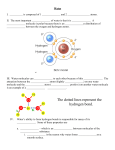
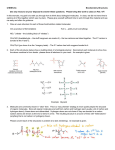
Chemical Reactions What is a chemical reaction? • A chemical reaction is a chemical change where chemical substances (called reactants) react to give new chemical substances (called products). • Example – The combustion of hydrogen in oxygen is a chemical reaction which gives water. • Hydrogen and Oxygen are the reactants. • Water is the product. Chemical reaction and molecules • The chemical reaction of hydrogen and oxygen is done between the molecules of these two gases. • In this chemical reaction, the bonds of the hydrogen molecules H2 and oxygen molecules O2 break down. • The atoms H and O form new bonds to give water molecules H2O. The three molecules • Hydrogen molecule H2 is made up of 2 atoms • Oxygen molecule O2 is made up of 2 atoms • Water molecule H2O Chemical equation • A chemical equation is a way which represents the rearrangement of the atoms during a chemical reaction. • In a chemical equation, we write the formulas of the reactants and the formulas of the products separated by an arrow. hydrogen + oxygen H2 + + O2 water H2O Lavoisier’s Law • Antoine Lavoisier, a french chemist, stated the following law: – « the number of atoms in the reactants = the number of atoms in the products. » • This law makes it possible to balance chemical equations Balance a chemical equation H2 + O2 H2O - There are 2 atoms H and 2 atoms O in the reactants. - There are 2 atoms H and 1 atom O in the product. To balance this equation, we take 2 water molecules containing 2 atoms O and 4 atoms H, and we take 2 hydrogen molecules and 1 oxygen molecule. H2 and H2 + O2 H2O and H2O We should write it: 2 H2 + O2 2 H2O To read a chemical equation 2 H2 + O2 2 H2O Read this equation as follow: 2 hydrogen molecules react with 1 oxygen molecule to form 2 water molecules. Attention: - The number of atoms is the same in the reactants and the products. - The number of molecules is not necessarily the same. Problems 1. Methane CH4 reacts with oxygen O2 to form carbon dioxide CO2 and water H2O. a. Balance the equation of this reaction CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O b. Determine the number of reactants and products molecules. Problems 2. Balance and read the following equations: a. b. c. d. Na Fe N2 Al + + + + O2 Cl2 H2 O2 Na2O FeCl3 NH3 Al2O3 Note : FeCl3 = Iron III chloride NH3 = Ammonia Al2O3 = Aluminum oxide Answers 1. CH4 + 2 O2 CO2 + 2 H2O 1 methane molecule react with 2 oxygen molecules to form 1 dioxide carbon molecule and 2 water molecules. answers 2. a. 4Na + O2 2 Na2O 4 sodium molecules react with 1 oxygen molecule to form 2 sodium oxide molecules. b. 2Fe + 3Cl2 2FeCl3 2 iron molecules react with 3 chlorine molecules to form 2 iron III molecules. Answers c. N2 + 3H2 2NH3 1 nitrogen molecule react with 3 hydrogen molecules to form 2 ammonia molecules. d. 4Al + 3O2 2Al2O3 4 aluminum molecules react with 3 oxygen molecules to form 2 aluminum oxide molecules.