* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Outline15 Spinal Cord
Survey
Document related concepts
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
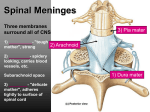
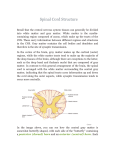
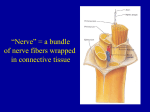
Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Clemens Nervous System 2 – Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves A. Spinal Cord 1. Meninges a. dura mater b. arachnoid mater c. pia mater Text: Chapter 17 spaces epidural space subdural space subarachnoid space denticulate ligaments filum terminale 2. External Anatomy of the Spinal Cord - adult spinal cord extends from foramen magnum to vertebra L2 cervical enlargement lumbar enlargement conus medullaris cauda equina 3. Internal Anatomy of the Spinal Cord anterior median fissure posterior median sulcus central canal gray matter posterior (dorsal) gray horn - sensory anterior (ventral) gray horn - somatic motor lateral gray horn - autonomic motor gray commissure white matter posterior white columns - sensory (ascending) tracts lateral white columns - sensory (ascending) and motor (descending) tracts anterior white columns - ascending and descending tracts roots of spinal nerves dorsal root - sensory ventral root - motor B. Spinal Nerves 31 pairs: cervical C1-C8 (exit above the same-numbered vertebrae) thoracic T1-T12 (exit below the same-numbered vertebrae) lumbar L1-L5 (exit below " " ) sacral S1-S5 (exit through the sacral foramina) coccygeal Co1 1. Connective tissue coverings epineurium - surrounds the nerve perineurium - surrounds fascicles endoneurium - surrounds individual axons 2. Branches of spinal nerves anterior ramus posterior ramus rami communicantes 3. Dermatomes 4. Plexuses Nerve examples: cervical plexus (C1-C5) phrenic nerve brachial plexus (C5-T1) median nerve, radial nerve, ulnar nerve lumbar plexus (L1-L4) femoral nerve sacral plexus (L4-S4) sciatic nerve Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Clemens Study Questions 1. 2. Describe the major anatomical features of the spinal cord as seen in a cross-section. Name and describe the meninges of the spinal cord. What are the names of the spaces between the meninges, and what is contained in these spaces? What is contained in the epidural space? 3. Diagram the arrangement of the gray matter and the white matter of the spinal cord. 4. Distinguish between the anterior (ventral) and posterior (dorsal) gray horns in terms of function and what types of neurons are located within them. 5. What type of information is carried by ascending tracts? What type of information is carried by descending tracts? Are these tracts in the gray matter or the white matter? Indicate which of the following are ascending tracts and which are descending tracts: lateral corticospinal tracts • posterior white columns • anterior corticospinal tracts 6. Describe the general structure of spinal nerves and their connective tissue coverings. 7. What type of information is carried by the dorsal (posterior) roots of spinal nerves? What type of information is carried by the ventral (anterior) roots of spinal nerves? 8. What effectors are innervated by somatic motor neurons? What effectors are innervated by autonomic motor neurons? 9. What is a dermatome and what is its clinical significance? 10. List the four principal spinal nerve plexuses and name one major nerve that arises from each plexus. Name three nerves that arise from the brachial plexus. 11. In the following table, identify the locations of the neural components of a reflex arc in relation to specific structures in the CNS (spinal cord) and PNS. Refer to Fig. 17.12 in your textbook. (The first two lines are filled in as examples.) CNS or PNS Specific location sensory neurons: dendrites PNS at sensory receptors axons PNS in spinal nerves cell bodies _____ axon terminals _____ integrating center: interneurons _____ motor neurons: cell bodies _____ axons _____ axon terminals _____