* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Adaptive Radiation
Rotating locomotion in living systems wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
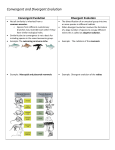
Adaptive Radiation Chapter 19 Ecological Niche The role an organism plays within a community Includes feeding, habitat, competitors, enemies etc Darwin’s finches - Galapagos Islands, 1831 - found many different species - large variety of beak size & shape - occupied many different niches (lack of competitors) - speciation lead to sub-populations - each became diversified and adapted to their niche Adaptive Radiation Evolution of a group of related organisms along several different lines - over a long period of time - to a wide variety of environments 1) marsupials in Australia - evolved into a variety of niches - no threat of competition from mammals 2) British buttercups - 3 species - all suited to different soil moistures Homology & Divergent evolution Homologous structures - same evolutionary origin - structurally alike E.g. mammals have pentadactyl (5 digit) limbs - limb has evolved to suit different functions (digging in moles, swimming in whales) This is divergent evolution Convergent evolution Animals that have similar structural features, but are from different ancestors E.g. european/strand moles are placental, marsupial mole is marsupial Evolve this way to suit their chosen niche