* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 15 - Western High School
Rotating locomotion in living systems wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
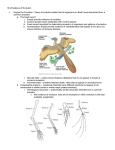
Chapter 15 Evolution Section 15.1 • Darwin’s Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection – Charles Darwin developed a theory of evolution based on natural selection – Darwin on the HMS Beagle – Galapagos Islands – Artificial selection: (selective breeding)-the process of directed breeding to produce offspring with desired traits Natural Selection • Those better equipped for survival are able to reproduce • Four basic principles – Individuals in a population show differences or variations – Variations can be inherited – Organisms have more offspring than can survive on available resources – Variations that increase reproductive success will have a greater chance of being passed on Natural Selection • Given enough time, natural selection could modify a population enough to produce a new species • Figure 15.3 page 421 Natural selection in a sunflower Basic Principles of Natural Selection • Individuals in a population show variations among others in the same species • Variations are inherited • Animals have more young than can survive on the available resources • Variations that increase reproductive success will be more common in the next generation The Origin of Species • Book written by Darwin compiling his work • Evolution used to define cumulative change in groups of organisms through time • Natural selection is not synonymous with evolution: it is a mechanism by which evolution occurs Section 15.2 • The theory of evolution states that all organisms on Earth have descended from a common ancestor • Evidence of Evolution – Multiple lines of evidence support the theory of evolution • • • • • The fossil record Comparative anatomy Comparative embryology Comparative biochemistry Geographic distribution The fossil record • Derived traits – newly evolved structures (feathers) do not appear in the fossils of common ancestors • Ancestral traits – more primitive features (teeth, tails) that do appear in ancestral forms Comparative Anatomy • Homologous structures – anatomically similar structures inherited from a common ancestor (reptiles and birds) • Vestigial structures – structures that are the reduced forms of functional structures in other organisms (snake pelvis, kiwi wings, human appendix) Comparative Anatomy • Analogous structures – structures that can be used for the same purpose and can be superficially similar in construction but are not inherited from a common ancestor (wings of eagle vs. wings of beetle) Comparative Embryology • Bird and mammal embryos share several developmental features – Tails – Pharyngeal pouches Comparative Biochemistry • Amino acid sequences – Cytochrome c – Figure 15.9 page 427 Geographic Distribution • Biogeography – the field of study that links climate and geological forces (plate tectonics) to ancestral relationships and geographic distribution seen in fossils and living organisms today Adaptation • Types – Camouflage • Ability to blend in with environment – Peppered moths – Mimicry • One species evolves to resemble another – California Kingsnake and Western Coral Snake – Antimicrobial resistance • Some species of bacteria have developed drug resistance – MRSA Consequences of Adaptations • Not all features of an organism are necessarily adaptive. • Some features might be consequences of other evolved characteristics – Spandrel • Architectural consequence to support dome – Human • Helplessness of human babies • Ability to walk upright and big brains