* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download this link starts first one 1) Isn`t evolution just a theory? What I think: 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
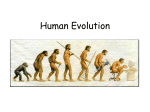
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=85diEXbJBIk this link starts first one 1) Isn’t evolution just a theory? 2) Who was Charles Darwin? What I think: What I think: 3) How do we know what happened? What I think: Notes from video: Notes from video: Notes from video: Evolution isn’t JUST a theory any more than gravity is JUST a theory. A theory is an explanation for a large body of evidence. There is a large and growing body of evidence for evolution. We can never prove it, but we can continue to put together the pieces of evidence to tell the story of how life evolved. An English naturalist. He was the one to come up with the concept of evolution by natural selection, and the connectedness of all organisms to a single common ancestor. He sailed The HMS Beagle to the Galapagos Islands and studied the differences between the similar species on the various islands. This gave him information to understand how new species formed from common ancestors on the mainland. Fossils are the main source of evidence for evolution. Fossils tell the story of the evolution of whales from a wolf-like creature. 4) How does evolution really work? What I think: 5) Did humans evolve? What I think: 6) Why does evolution matter now? What I think: Notes from video: Notes from video: Notes from video: The mechanisms for natural selection are: Genetic variation. For example, hummingbirds of a same species can be born with different length beaks. Overproduction of Offspring. For example, an adult hummingbird may have dozens of babies over a lifetime, but only a few (the ones with the best adaptations) are expected to survive. Struggle for existence. For example, the hummingbirds may compete with each other for the nectar from the local flowers. Differential Survival and Reproduction. For example, the hummingbirds with the optimal beak length will survive to pass their genes down to the next generation. Yes, humans evolved, but we did not evolve FROM apes. We and apes have a recent (in evolutionary terms) common ancestor. DNA evidence shows that we have very similar DNA to chimpanzees. This shows that humans and chimpanzees are the most recently branched in the primate family. Because it is still happening every day. Bacteria are quickly evolving resistance to antibiotics, creating “superbugs” that can no longer be treated (as in a strain of TB spreading through Russian prisons). We use our knowledge of how evolution works to continue the battle against antibioticresistant bacteria.