* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Eng - Healthier SF
Survey
Document related concepts
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
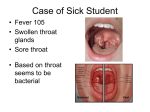
Date: Dear Parent/Caregiver: A student in your child’s class has been recently diagnosed with “strep throat.” Not all sore throats are caused by streptococcal bacteria, but those that are must be treated with antibiotics for the prescribed length of time to avoid complications from the “strep” bacteria. What to look for: Group A streptococcal bacteria can cause a sore throat, fever, stomachache, headache, swollen glands in the neck and decreased appetite. When “strep throat” is accompanied by a fine, red rash that makes the skin feel like sandpaper, then the infection is referred to as “scarlet fever”. The presence of the rash does not increase the severity of the disease. Incubation period: The incubation period is from 2 to 5 days after exposure to the disease. What to do for your child with sore throat and rash: If your child has a severe sore throat with or without a rash or a severe sore throat that lasts more than 24 hours and is not associated with other cold symptoms, your child must be seen by a health professional to determine if the cause is “strep throat.” The health professional will do a throat culture to see if there is streptococcal bacteria in the throat and will prescribe antibiotics based on the results. Exclusion period: The child is no longer contagious after s/he has been on antibiotics for 24 hours. A child can return to school when he/she is feeling better and after 24 hours of antibiotic treatment. How is streptococcal infection spread: “Strep” infection is spread by direct contact and by exposure to respiratory droplets from an infected person. Good hand-washing can prevent further spread of the disease. Please contact your child’s health professional if you have any further questions. Student, Family and Community Support Department 2015-2016 School Health Manual