* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics - Science 7
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
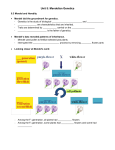
Chapter 4: Genetics: The Science of Heredity Section 1: Mendel’s Work Gregor Mendel’s work was the foundation for understanding why offspring have traits similar to those of their parents. Mendel’s Experiments Mendel used purebred plants, which always produce characteristics similar to their parents. Homozygous- same letter designation representing traits.(TT, tt, DD,dd) (Filial-son in Latin) Mendel, an Austrian monk in the 1850’s, worked with pea plants and identified characteristics. By controlling pollination and through careful data collecting Mendel is often referred to as the Father of Genetics. Dominant and Recessive Alleles Genes are the factors that control traits. Different forms of a gene are called alleles. Individual alleles control the inheritance of traits. Some alleles are dominant, while other alleles are recessive. Dominant- a trait that always shows up when the allele is present. Recessive- is masked, or covered up whenever the dominant allele is present. Hybrid- two different alleles resulting in dominant appearance. Also called heterozygous.(Tt, Dd) Traits are controlled by alleles of genes. Organisms inherit one allele from each parent. Opener:Take a Class Survey Lab Pg.76-77 Section 2: Probability and Genetics Probability is the likelihood that a particular event will occur. (Coin flip) Mendel was the first scientist to interpret his data using the principles of probability. Geneticists use Punnett squares to show all the possible outcomes of a genetic cross. Punnett squares allow a person to determine the probability of a particular outcome. Phenotype- physical appearance Genotype- genetic makeup ( ie: allele assortment) w w b b Codominance- occurs when neither allele is dominant or recessive. F F (white feathers) F F (black) Skills Check: Construct a Punnett square for a cross between two heterozugous Erminette chickens that show all the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. Calculate the probabilities of each genotype and phenotype. b w Erminette Chicken- F F