* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3 MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Objectives After completing this exercise
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
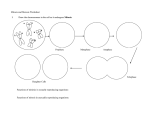
3 MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Objectives After completing this exercise you should be able to 1. Describe the sequential events in the cell cycle during. 2. List the main stages of meiosis. 3. Know basic differences in mitosis and meiosis. Introduction The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell division. The cell division process is an integral part of the cell cycle that results in the production of genetically identical daughter cells. Cells duplicate their genetic material before they divide, ensuring that each daughter cell receives an exact copy of the genetic material, DNA. Cell division functions in 1) Reproduction 2) Growth 3) Repair The eukaryotic genome consists of a number of DNA molecules packaged in chromosomes. Chromosomes are made of chromatin, a complex of DNA and protein. Somatic cells have two sets of chromosomes, while gametes have one set of chromosomes. Structure of chromosome Cell Division Is of two types – 1) Mitosis and 2) Meiosis 1) Mitosis – Is division of somatic cells to produce identical somatic cells. It involves division of the nucleus, karyokinesis and division of the cytoplasm, cytokinesis 2) Meiosis – Is a specialized cell division of somatic cells to produce gametes. It involves reduction of the chromosome number to half. It also involves karyokinesis and cytokinesis. Mitosis The cell cycle during mitosis consists of two phases: 1) Interphase and 2) The mitotic phase The mitotic phase alternates with interphase in the cell cycle 1) Interphase : Is cell growth and copying of chromosomes in preparation for cell division, Is divided into subphases i) G1 phase (first gap) ii) S phase (synthesis) iii) G2 phase (second gap) 2) The mitotic phase: Consists of i) mitosis and ii) cytokinesis i) Mitosis is subdivided into 4 sub phases - Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase. EXERCISE 1) Study the models of mitosis to differentiate between the prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. 2) Observe the White fish blastodisc slide to study and identify the prophase, metaphase anaphase and telophase. Whitefish Blastodisc a) Prophase b) Metaphase c) Anaphase d) Telophase Meiosis Meiosis occurs in gonads, the testes and the ovaries for the formation gametes, the sperms and ova. Takes place in two sets of divisions: 1) Meiosis I and 2) Meiosis II 1) Meiosis I: Results in two haploid daughter cells with replicated chromosomes; it is called the reduction division. Homologous chromosomes separate during this phase and the sister chromatids are together. This phase is subdivided into Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I and Telophase I. 2) Meiosis II: Is the second cell division during which sister chromatids in each of the two cells separate resulting in four haploid daughter cells; it is called the equational division. This phase is subdivided into Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II and Telophase II.