* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download I. Rise of the Axis Powers (Germany, Italy, Japan)
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
The War That Came Early wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
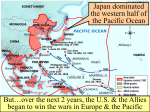
A.P. United States History Chapter 23, Americans and the World in Crisis Notes I. Rise of the Axis Powers (Germany, Italy, Japan) A) Germany (post WWI disillusionment=rise of NAZIS/ A. Hitler) B) Italy (post WWI disillusionment=rise of Fascists/B. Mussolini C) Japan (US Open Door Policy, Japanese overpopulation/lack of resources=Japanese invasion of China 1931=US sanctions esp OIL) II. World War II Begins, 1939-1942 A) Sept 1, 1939, after signing Non-Aggression Pact with USSR Germany invaded Poland; England/France declared war on Germany (phony war/sitzkrieg) B) U.S. Neutrality Acts of 1935 banned loans, travel or sales of arms to belligerents (no help for allies) C) Sept 21, 1939 Neutrality Acts aka Cash and Carry policy amended with U.S. policy D) May 10, 1940, Germans invaded/occupied Denmark, Norway, Belgium, Holland, Luxembourg and France E) June 1940, allies driven into English Channel at Dunkirk F) July 1940-October 1940, the German Luftwaffe bombed England (Operation Sea Lion, Battle for Britain) G) Sept 19, 1940, U.S. began 1st peacetime draft H) Nov 1940, FDR elected to his 3rd term I) March 1941, Lend Lease Act amended the Neutrality Acts authorizing the president to transfer weapons to “the government of any country whose defense the President deems vital to the defense of the United States.” J) June 1941, breaking Non-Aggression Pact, Germany invaded USSR; USSR joined Allies K) Aug 1941, Allies(?) met/wrote Atlantic Charter (condemned aggression, supported self-determination, free trade, disarmament and collective security) L) Dec 7, 1941, Japan attacked Pearl Harbor; Germany/Italy declare war on US III. America Mobilizes at Home A) Gov est. agencies to control production/consumption of goods, to prevent inflation and “sell” the war B) US became the “Arsenal of Democracy” thru war production C) Depression ended as thousands of new jobs available esp for women D) Feb 1942-March 1946 by Exec. Order 110,000 Japanese (62% US Citizens and 38% immigrants were interned in guarded camps E) Korematsu v. US=Supreme Court upheld US government policy IV. WWII in Europe and North Africa, 1942-1944 A) Nov 1942, Allied invasion of N. Africa; May 1943 Germans surrendered B) Jan 1943, FDR met Churchill at Casablanca, agreed to invasion of Italy before France C) Feb 1943, Soviets defeated the Nazis at the Battle of Stalingrad D) Sept 1943, Allied invasion of Italy E) Nov 1943, Big Three met at Tehran, agreed to invasion of France, post-WWII division of Germany, USSR to declare war on Japan after German defeat F) June 6, 1944, D-Day invasion of Normandy, France G) Nov. 1944, FDR re-elected to 4th term V) WWII the Pacific, 1942-1945 A) June 1942, U.S. defeated Japanese at Battle of Midway ending Japanese expansion B) US led by Gen MacArthur used Island Hopping strategy to defeat Japanese C) June 1945, Allied forces in Okinawa (350 m. from Japan) VI. End of the War, 1945 A) Feb 1945, Big Three met in Yalta; agreed to UN, 3 month deadline for USSR to declare war on Japan, “representative” govs in E. Europe B) April 12, 1945, FDR died; Harry Truman=president C) April 25, 1945, US and Soviet troops met in Germany D) May 8, 1945, Hitler committed suicide; Germany surrendered E) July-August 1945, Big Three, met at Potsdam (news of Abomb delivered to Truman in July) F) Aug 1945 facing a US invasion of Japan, Truman opted to use the A-bomb (6th: Hiroshima/8th Nagasaki) G) August 8, USSR declared war on Japan as agreed at Yalta H) Aug 14, 1945, Japan surrendered