* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 14 and 15 Notes-WWII
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
The War That Came Early wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
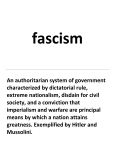
U.S. History Unit 4, Chapters 14 and 15 World War II Notes I. Rise of the Axis Powers (Germany, Italy, Japan) A) Germany: 1920s-30s, rise of NAZI Adolf Hitler=1933, became Chancellor and used his Brown Shirt Army (SA) to suppress opposition in Germany B) Italy: 1920s-30s, rise of the fascist Benito Mussolini C) Japan: 1931, started its expansion in the Pacific with invasion of China (Manchuria) which US reacted to negatively (eventually US cut oil sales to Japan in protest) II. German Aggression and World War II Begins A) 1936, Germany (remilitarized) the Rhineland B) 3/1938, Germany annexed Austria C) Summer 1938, Hitler demanded the German populated Sudetenland (part of Czech) D) 9/1938, GB and France agree Hitler’s demand for the Sudetenland for peace (Appeasement) E) 1939, Germany takes all of Czechoslovakia F) 8/1939, Germany and USSR agreed to a NonAggression Pact G) Sep 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland and GB and France declare war. III. American Response (Before Battle of Britain) A) 1930’s, most Americans favored Isolationism B) 1930’s, Congress passed Neutrality Acts which prohibited loans, weapons sales, traveling on ships of nations at war C) Sept 21, 1939, Neutrality Acts amended allowing Cash and Carry plan to any nation IV. European Front (1940) A) May 1940, Germans invaded/occupied Denmark, Norway, Belgium, The Netherlands, Luxembourg and France B) Fall 1940, Hitler began the Bombing of Britain; sends aid to Mussolini in North Africa V. American Response (after Battle of Britain) A) Oct 1940, Selective Training and Service Act was passed (1st peacetime draft in U.S.) B) Nov 1940, FDR elected to his 3rd term C) Dec 29, 1940, FDR’s Fireside Chat calls for American support of the Allies * Arsenal of Democracy Speech D) 1/16/41, FDR’s State of the Union Speech aka Four Freedoms Speech * Four Freedoms Speech E) Mar 1941, Lend Lease Act authorized FDR to “sell, transfer, exchange, lease, or lend any weapons/supplies in defense of US VI. The USSR enters the War A) 6/1941, Germany invaded USSR (defacto Ally) B) 9/1941, FDR and Churchill agreed to the Atlantic Charter VII. The US enters the War A) Japanese expansion =US protest and embargo on naval, aviation supplies OIL, iron, steel, etc. B) Dec 7, 1941 Japan attacked US Naval base at Pearl Harbor killing 2500 C) Dec 8, 1941, U.S. declared war on Japan, Germany and Italy declared war on US VIII. American Mobilizes for World War II A) Government est. agencies to oversee production and consumption of goods, to prevent inflation and “sell” the war B) Income taxes were raised; payroll deduction system started C) Science and technology for war resulted in civilian uses D) Depression ended, new jobs available especially for women E) Japanese Internment: 110,000 Japanese Americans (62%) and Japanese immigrants from the West Coast were interned in guarded camps F) Korematsu v. US=supreme court upheld US government policy IX. The Allies turn the Tide, 1942-1944 in Europe A) 1942 German invasion of USSR was defeated; on to Berlin B) May 1943, Allied troops invaded North Africa; defeated Axis C) Summer 1943, Allies invaded Italy; on to Berlin D) June 6 1944, Allied invasion of France/Normandy began (D-DAY); on to Berlin X. WWII in the Pacific, 1942-1945 A) June 1942, U.S. defeated Japanese at Battle of Midway ending expansion of Japanese empire (turning point) B) US led by Gen MacArthur used “Island Hopping” strategy to force Japanese back to Okinawa (350 m. from Japan) by June 1945 XI. End of the War in Europe A) Nov. 1944, FDR re-elected to 4th term B) Feb 1945, FDR, Churchill and Stalin met at Yalta and agreed to 1) formation of the UN 2) 3 month deadline for USSR to enter Pacific War 3) “representative” governments in E. Europe C) April 1945, US and Soviet troops met in Germany D) April 12, 1945, FDR died; Harry Truman= president E) May 8, 1945, Hitler committed suicide in his Berlin bunker; Germany surrendered (VE Day) XII. End of the Pacific War, 1945 A) July to Aug 1945, Truman, Churchill (later Atlee), and Stalin, met at Potsdam; Truman learns of the successful A-bomb test B) Truman opted to use the A-bomb against Japan (Aug 6=Hiroshima, Aug 8=Nagasaki) D) Aug 8, as promised the USSR declared war on Japan E) Aug 14, 1945, Japan surrendered (VJ Day) XIII.The Post-World War II World A) The United Nations was est. B) Germany and Berlin were divided into 4 zones occupied by the big 4 C) U.S. and USSR emerged from WWII as “Superpowers”