* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Insect Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
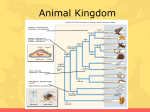
Animal Notes Animal Characteristics: - Eukaryote - Sexual reproducers - Heterotrophs - Locomotion (walk, fly, swim) - Multicellular 2 Phylum of Animals: No backbone. - Examples are: insects, worms, sponges, mollusks, and etc. - Lack: bones, some have hard outer shells or exoskeletons - 95% of all animals - Insects make up 80% of all animals. Chordata- 5 divisions of chordata - Make up only 5% of all animals. 5 Classes of the Phylum Chordata: 1. Fish 2. Amphibians 3. Reptiles 4. Birds 5. Mammals Fish: - Habitat: nearly every aquatic environment Respiration: use gills to breathe Circulation: 2 chambered heart Reproduction: sexual (mostly external) Nervous System: lateral line system that can detect movement Amphibians: - Habitat: live on land and water - Respiration: lungs in adults, gills in tadpoles, but mostly through the moist skin - Reproduction: external reproduction (water needed to transport sperm and eggs must be kept moist) - Circulation: 3 chambered heart. One chamber gets oxygen rich blood from lungs and skin. - Regulation: Ectotherms, variable body temperature- gets heat from outside source - Metamorphosis: eggs, tadpoles, adult Reptiles: - Habitat: Land mostly - Respiration: No exchange thru skin because it is scaly. Must use lungs - Circulation: most have 3 chambered heart - Regulation: ectotherms - Reproduction: Internal fertilization and can lay eggs on land due to the evolution of the amniotic egg Birds: - Respiration: Lungs and air sacs for extra oxygen for flight Regulation: Endotherm Reproduction: Internal fertilization Adaptations: Hollow bones for flight, feathers are lightweight, wings - Circulation: 4 chambered heart Mammals: - Special characteristics needed: hair, mammary glands that secrete milk to nurse young, diaphragm to expand and contract chest activity to get more oxygen, specialized teeth (molars, canines, incisors), can learn - Regulation: endotherms, maintain fairly constant body temperature - Circulation: 4 chambered heart, the oxygenated blood is kept separate from the deoxygenated blood - Respiration: - sheet of muscle located beneath the lungs that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity - Hair importance: insulation, waterproofing, conserves body heat, mammals cool off by panting and sweating 1. Placental mammals: carries baby in the mothers uterus until development is almost complete 2. Marsupials: after a baby has grown to a certain size, the mom carries the baby inside a pouch made of skin and hair on th outside of the moms body 3. Monotremes: reproduce by laying eggs. Found in Australia, Tasmania, and New Guinea. 3 species of monotremes alive today (platypus, spiny anteater and long beaked echidna