* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download L4 The LARGE INTESTINE
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
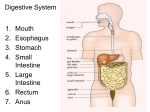
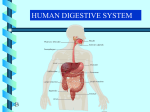
L4 Outline 1. Mark Enzymes worksheet 2. Notes on large intestine 3. Notes on problems with large intestine 1. Fibre 2. Diarrhoea 3. Constipation 4. Finish video on digestion L4 Quiz Small Intestine 68 1. What is each number? 1. Duodenum or small intestine 2. Pancreas 3. Stomach 4. Cardiac sphincter or esophagus L4 Quiz Small Intestine 69 2. What green liquid is inserted into the upper small intestine? bile L4 Quiz Small Intestine 70 3. What enzyme is secreted by the small intestine? Lipase L4 Quiz Small Intestine 71 4. What are the two main jobs of the small intestine? Digestion and absorption L4:The Digestive Process - Defecation How does the body process food? The large intestine is about 1.5 meters long, containing undigested material including fiber, bacteria and other wastes that have been passed from the small intestine. It's here, that water is extracted (recycled) and the waste material is finally processed before elimination. L4 The LARGE INTESTINE The large intestine (colon) extends from the ileocecal sphincter to the anus; the medical specialty that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of disorders of the rectum and anus is called Proctology. L4 The LARGE INTESTINE Its subdivisions include the cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal. cecum rectum anal canal colon L4 The LARGE INTESTINE Processes occuring in the large intestine • bacterial breakdown of food • bacteria synthesize some vitamins which are absorbed • water is absorbed • electrolytes are absorbed L4: The LARGE INTESTINE Feces consist of • water • inorganic salts • sloughed-off epithelial (skin) cells • bacteria • products of bacterial decomposition • undigested parts of food L4 The LARGE INTESTINE Although most water absorption occurs in the small intestine, the large intestine absorbs enough to make it an important organ in maintaining the body’s water balance. L4 The LARGE INTESTINE The elimination of feces from the rectum is called defecation. Defecation is a reflex action aided by voluntary contractions of the diaphragm and abdominal muscles. ¨ Diarrhea refers to frequent defecation of liquid feces. It is caused by increased motility of the intestine and can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. ¨ motility of=movement of food through L4 The LARGE INTESTINE Problems Constipation refers to infrequent or difficult defecation and is caused by decreased motility of the intestines, in which feces remain in the colon for prolonged periods of time. Caused by • low fibre • resisting defecation • low excercise • low liquid intake • medications Can cause • hemorrhoids • anal fissure • rectal prolapse • fecal impaction • vomiting (uh oh) Prevent by • eating high fibre • lots of liquids • excercise • use the toilet when you get the urge L4 The LARGE INTESTINE Dietary fiber (bulk of roughage) Two types soluble and insoluble. Both types affect the speed of food passage through the GI tract. Benefits • protects vs colon cancer • lower blood cholesterol • reduces constipation • prevents diverticulosis L4 The LARGE INTESTINE ¨ 1. Watch video on digestive system