* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bryophytes and Ferns
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
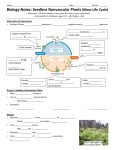
Bryophytes and Ferns January 31, 2008 Vocabulary Bryophytes Hornworts Antheridium Microspores Hepatophyta Anthocerophyta Gametophore Protonema Sporangium Fronds Sporophylls Lycophyta Pterophyta Bryophyta Liverworts Rhizoids Archegonium Sorus Megaspores 1. Which of the following characteristics do mosses, liverworts, and hornworts share? a. reproduction in gametangia; embryos b. vascular tissues, true leaves, and a waxy cuticle c. seeds 2. Which of the following is diploid? a. the archegonia of a moss b. a cell in the gametangia of a moss c. a cell that is part of the stalk of a moss sporophyte d. a spore produced by a sporophyte 3. In moss, _____ produce sperm. a. sporangia b. antheridia c. embryos d. archegonia 4. Fertilization in moss occurs when sperm swim from a(n) _____ to a(n) _____. a. antheridium ... sporangium b. sporangium ... antheridium c. antheridium ... archegonium d. archegonium ... antheridium e. sporangium ... archegonium 5. The gametophyte generation of a moss _____. a. produces spores b. is dependent on the sporophyte c. is haploid d. is rarely encountered, compared with the sporophyte 6. The sperm produced by mosses require _____ to reach an archegonium. a. wind b. light c. moisture d. the development of a flower e. animals 7. In the moss life cycle _____ cells within a sporangium undergo _____ to produce _____ spores. a. diploid ... meiosis ... haploid b. haploid ... mitosis ... haploid c. diploid ... mitosis ... diploid d. diploid ... mitosis ... haploid e. haploid ... meiosis ... haploid 8. Plants undergo alternation of generations in which _____. a. the sporophyte generation alternates with the gametophyte generation b. the vascular generation alternates with the nonvascular generation c. male plants alternate with female plants d. antheridia alternate with archegonia e. all of these occur 9. In mosses, haploid _____ directly produce buds that grow into gametophores. a. archegonia b. antheridia c. spores d. gametophytes 10. Mosses are limited mostly to moist environments because _____. a. their pollen is carried by water b. they lack vascular tissue c. they have swimming sperm d. their seeds do not store water e. they desiccate easily 11. The conspicuous part of a fern plant is a _____. a. haploid gametophyte b. diploid gametophyte c. diploid sorus d. diploid sporophyte e. haploid sporophyte 12. In the life cycle of a fern, the multicellular male gametangium (the sex organ that produces sperm cells) is called a(n) _____. a. antheridium b. archegonium c. frond d. sporangium 13. Fern gametophytes are _____. a. photosynthetic diploid organisms b. produced from haploid gametes c. part of the asexual life cycle d. free-living, multicellular organisms e. found on the underside of fern leaves (fronds) 14. Which of the following is not common to all phyla of vascular plants? a. the development of seeds b. alternation of generations c. dominance of the diploid (sporophyte) generation d. xylem and phloem e. sporophyte that is independent of the gametophyte 15. Which of the following is a land plant that produces flagellated sperm and has a sporophyte-dominant life cycle? a. fern b. moss c. liverwort d. charophycean e. hornwort 16. The "dots" on the underside of a fern frond are spore cases; therefore, what is true of the plant to which the frond belongs? a. It is a spore. b. It is a gamete. c. It is a sporophyte. d. It is a gametophyte. e. It is a spermatophyte. 17. To examine meiosis in ferns, you would study _____. a. the antheridia b. the archegonia c. the sporangia d. both the antheridia and the archegonia e. both the archegonia and the sporangia 18. Microsporangia produce microspores, which produce _____ that produce _____. a. Female gametophyte, eggs b. Female gametophyte, sperm c. Male gametophyte, eggs d. Male gametophyte, sperm 5. Fill in the following table to compare bryophytes to ferns (and related groups). Bryophytes Ferns Clades included Dominant stage Relative gametophyte size Vascular tissue? Seeds? Branched sporophytes? Is a life stage dependent? Needs moisture? Why? Meiosis Fertilization Life Cycle of Moss Life Cycle of Fern