* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download During WS - SCSC Year 10 Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
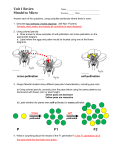
Genes and Inheritance During the Program 1. What are genes? Where are they located? 2. Identify some examples of the characteristics that genes control. 3. In Mendel’s work with pea plants, what was the result of crossing pure-bred tall plants with a pure-bred short plants? 4. What are gametes? 5. What are alternative forms of genes called? 6. Explain Mendel’s first law. 7. Explain the difference between homozygous and heterozygous. © ClickView Pty Limited 2014 Reproducing these support notes You may download and print one copy of these support notes from ClickView for your reference. Further copying or printing must be reported to CAL as per the Copyright Act 1968. 8. Explain the concept of dominant and recessive alleles in relation to Mendel’s work referred to in question 3 above (ie why did he get the results he did?) 9. Define phenotype and genotype. 10. Complete the Punnet squares: a) The crossing of a pure-bred tall pea plant and a pure-bred short pea plant - P1 generation - TT x tt Male T T Female t t b)The crossing of two heterozygous offspring (F1 generation): Male T t Female T t Ratio of tall phenotypes to short phenotypes = __________________ © ClickView Pty Limited 2014 Reproducing these support notes You may download and print one copy of these support notes from ClickView for your reference. Further copying or printing must be reported to CAL as per the Copyright Act 1968. c) A dihybrid cross involving pea plants with round, yellow peas: Male gametes Female gametes RY Ry rY ry RY Ry rY ry Ratio of round yellow peas to round green peas to wrinkled yellow peas to wrinkled green peas = __________________________ 11. What genotypes would be possible for round yellow peas? (List them all). 12. What would be the phenotypes of peas with the following genotypes: a) rrYy b) Rryy c) Rryy d) RrYy 13. Explain Mendel’s second law. © ClickView Pty Limited 2014 Reproducing these support notes You may download and print one copy of these support notes from ClickView for your reference. Further copying or printing must be reported to CAL as per the Copyright Act 1968. 14. Provide an example of incomplete dominance, and an example of co-dominance. 15. Explain why it is often said that a father determines the gender of a child. 16. Using red/green colourblindness as an example, what is meant when it is said that a female can be a carrier of the condition, but not affected by it? 17. Approximately how many conditions have been shown to be sex-linked in humans? 18. What does it mean when certain genes are said to be linked? 19. Using body colour and wing length in Drosophila as an example, explain how crossing over can occur. (Use a diagram if you like) 20. What role do certain enzymes play in crossing over? Why is this important in populations of living things? 21. With a sex-linked condition like haemophilia, why can males never be carriers? 22. Albinism is an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. What does this mean? © ClickView Pty Limited 2014 Reproducing these support notes You may download and print one copy of these support notes from ClickView for your reference. Further copying or printing must be reported to CAL as per the Copyright Act 1968. 23. Explain the difference between monogenic and polygenic inheritance. Give examples of each. © ClickView Pty Limited 2014 Reproducing these support notes You may download and print one copy of these support notes from ClickView for your reference. Further copying or printing must be reported to CAL as per the Copyright Act 1968.