* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetic Inheritance Test
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
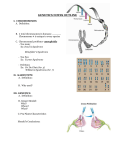
Student Name: ________________________________ Genetics/Inheritance Q1 What is a gamete? ____________________________________________________________________ What is its function? ___________________________________________________________________ Q2 Describe briefly what is meant by each of the following terms: Allele 2(1) marks __________________________________________________________________________ Dominant __________________________________________________________________________ Recessive __________________________________________________________________________ Genotype __________________________________________________________________________ Phenotype __________________________________________________________________________ Homozygous _________________________________________________________________________ Heterozygous ________________________________________________________________________ Incomplete dominance _________________________________________________________________ 8(2) marks Q3 Write down the resulting ratio you would expect in each of the following monohybrid crosses: (a) Two homozygous recessive parents _______________________________________________________ (b) One homozygous recessive parent and one heterozygous parent _______________________________ (c) Two heterozygous parents ______________________________________________________________ 3(2) marks Q4 Fill in the blanks in the cross shown to explain how it is equally likely to have a male or female child. 8(2) marks Q5 State the Law of Segregation ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ State the Law of Independent Assortment ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 2(2) marks Student Name: ________________________________ Q6 Write down the resulting ratio you would expect in each of the following di-hybrid crosses. No linkage is involved. (a) Two parents homozygous recessive for both characteristics ___________________________________ (b) One homozygous recessive parent and one heterozygous parent (for both characteristics) __________ (c) Two heterozygous parents (for both characteristics) _________________________________________ 3(2) marks Q7 Explain what is meant by the following terms: (a) Locus _______________________________________________________________________________ (b) Linkage _____________________________________________________________________________ (c) Sex Linkage __________________________________________________________________________ 3(2) marks Q8 Determine the four possible F1 generation genotypes in a cross between a haemophiliac (n) male and a heterozygous normal (N) female. ` 1 ______________________________ 3 ______________________________ 2 ______________________________ 4 ______________________________ State the phenotypes of these individuals ` 1 ______________________________ 3 ______________________________ 2 ______________________________ 4 ______________________________ 8(2) marks Q9 The allele for tongue rolling (R) is dominant to the allele for non tongue rolling (r). Also the allele for brown hair (B) is dominant to red hair (b). Neither of these characteristics is sex linked. Using the punnet square shown determine the possible F1 generation genotypes of a cross between two heterozygous parents (heterozygous for both characteristics). 28(1) marks