* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download obstetrics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
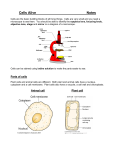
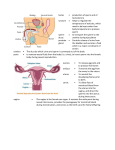
OBSTETRICS Obstetrics Is the science of dealing with the care of the pregnant women during all stages of pregnancy and the period following birth. An obstetrician is a person who specialises in obstetrics. Often doctors specialise in obstetrics and gynaecology. Root Combining form Meaning Obstetric Obstetr/ic midwife Pregnancy is the sequence of events including fertilisation, implantation, embryonic growth and normally, foetal growth that terminates in birth. Semen Is a mixture of sperm and secretions of the seminal vesicles and prostate. Insemination refers to the deposition of semen in the female reproductive tract. Artificial insemination (AI) refers to the insertion of semen into the uterus via a cannula instead of coitus. The sperm used in this procedure can be from two sources; AI by husband (AIH) – semen from the woman’s husband is used AI by donor (AID) - semen from a male other than the husband is used. Root Combining form Semin Semin/i Sperm Sperm/o, spermat/o, sperm/i Meaning Liquid secretion or semen of the testicles and glands associated with the reproductive system Sperm cells or spermatozoa, ejaculated from the male during the peak of sexual excitement Activity 1 Write the meaning of; 1. aspermia __________________________________________________________ 2. oligospermia _______________________________________________________ 3. spermicide _________________________________________________________ Build words using spermat/o which mean; 4. formation of sperm ___________________________________________________ Sperm counts are performed to estimate the number of sperm, the percentage of abnormal sperm and their mobility. The actual number of sperm is important in determining the fertility of the male. A sperm count of less than 60 million sperm per cm3 of semen results in decreased fertility, even though only one sperm is required to fertilise an egg. Fertilisation The term fertilisation, or conception, is applied to the union of the sperm and the ovum. Fertilisation normally occurs in the uterine tube when the ovum is about one third of the way down the tube. The fertilised ovum is called a zygote. The zygote moves down the fallopian tube and is implanted in the endometrium. Obstetrics Page 1 of 6 Occasionally, fertilised eggs can grow outside the uterus. These are known as ectopic pregnancies. The most common ectopic site is the fallopian tube. DEVELOPMENT OF FOETUS Embryo The first two months are considered the embryonic period. During this period the developing human is called an embryo. After the second month (8 weeks) it will be called a foetus. During the embryonic period the embryonic membranes form. These membranes lie outside the embryo and will protect and nourish the embryo and later the foetus. As the embryo grows the amnion, a thin protective membrane, surrounds it and becomes filled with amniotic fluid. Amniotic fluid serves as a shock absorber for the foetus. The amniotic sac ruptures just before birth and its fluid is known as the ‘bag of waters’. Root Combining form Amni Amni/o Chorion Chori/o Meaning Foetal membrane which retains the amniotic fluid surrounding the developing foetus Part develops into the placenta and part becomes closely aligned to the amnion Activity 2 Write the meaning of 1. amniogenesis ______________________________________________________ 2. amniocentesis ______________________________________________________ Foetus The part of the foetus, which lies in the lower part of the uterus, is known as the presenting part. In a normal birth the vertex of the skull forms the presenting part and it enters the birth canal first. Malpresentation is where other parts enter first. Placenta The placenta develops between the embryo and the endometrium (lining of the uterus) of the mother. It provides an exchange of nutrients and wastes between the foetus and the mother and secretes the hormones necessary to maintain pregnancy. Root Combining form Meaning Foet Foet/o An unborn baby Placent Placent/o Flat cake Adherent placenta – a placenta which is fused to the uterine wall so that separation is slow and delivery of the placenta is delayed/difficult Retained placenta – when the placenta is not expelled Placenta praevia – placenta forms abnormally in the lower part of the uterus over the internal opening of the cervix. Activity 3 Build words which mean; 1. Pertaining to poisoning of the foetus _________________________________ 2. Measurement of the foetus ________________________________________ 3. Inflammation of the placenta _______________________________________ Obstetrics Page 2 of 6 Umbilical cord The umbilical cord connects the foetus to the placenta and transports blood and nutrients. Gestation The time the embryo or foetus is carried in the uterus is called gestation. The total human gestation is about 280 days. Approximately 9 months. Root Combining form Meaning Gravida -gravida Para -para Toc Toc/o, -tocia Describes a woman in relation to her pregnancies Number of previous pregnancies, resulting in a live infant Birth/labour Nat Nat/o Birth Antenatal Refers to the period from conception until birth. Gravida is the term for a pregnant woman. The pregnancy is broken into three periods each about three months long and each called a trimester, ie, first trimester, second trimester, third trimester. Labour and delivery The term parturition refers to birth; a parturient is a woman in labour. Parturition is preceded by a sequence of events commonly called labour. ust prior to birth, the muscles of the uterus contract rhythmically and forcefully. Uterine contractions, called eutocia, occur in waves. They start at the fundus of the uterus and move downwards. These waves expel the foetus. If labour is late or slow an injection of syntocinon can produce forcible contractions. There are three stages of labour. The first stage, the stage of dilation, is the time from the onset of labour to the complete dilation of the cervix. During this stage there are regular contractions of the uterus, a rupturing of the amniotic sac and complete dilation of the cervix, 10 cm. The second stage of labour, the stage of expulsion, is the time from complete cervical dilation to delivery. In the third stage, the placental stage, the placenta (afterbirth) is expelled a few minutes after the delivery of the foetus. During labour the foetus is monitored, usually by its heartbeat, to identify any signs of distress. The foetus lies in a lateral position in the uterus and during labour its head moves down to engage with the cervix. The portion of the foetus that is touched by an examining finger through the cervix is called presentation. Usually it is the head (vertex). If the buttocks or feet are presented it is called a breech and the foetus may have to be turned in the uterus before delivery can occur otherwise a caesarian section is performed. The 6-8 weeks following birth is known as puerperium. It is the period when the reproductive system involutes (reverts) to its pre-pregnancy state. Puerperal sepsis is a serious infection of the genital tract occurring within 21 days of abortion or childbirth. Postpartum haemorrhage – excessive bleeding from the birth canal Eclampsia – sudden convulsion due to toxaemia of pregnancy Stillbirth – where the foetus is born dead Obstetrics Page 3 of 6 Congenital – present at the time of birth, eg. congenital heart disease is a structural heart defect present at the time of birth Caesarean section – delivery by way of a surgical incision through the abdominal wall Forceps – surgical instruments used in difficult labour to help delivery Activity 4 Write the meaning of; 1. Placentopathy ______________________________________________________ 2. Primigravida (gravida 1) _______________________________________________ 3. Multigravida ______________________________________________________ 4. Primipara (para 1) ___________________________________________________ 5. Multipara ______________________________________________________ 6. Dystocia ______________________________________________________ 7. Tocology ______________________________________________________ 8. Neonatal ______________________________________________________ 9. Antenatal ______________________________________________________ 10. Neonatology ______________________________________________________ Mammary glands The essential function of the mammary glands is milk secretion or lactation. The mammary glands are glands that lie over the pectoralis muscles and are attached to them by a layer of connective tissue. The amount of adipose (fat) tissue determines the size of the breast. Ducts convey milk from the lobes of the breast to the exterior. The circular, pigmented arc of skin surrounding the nipple is called the areola. Root Combining form Meaning Mast Mast/o Breast Mamm Mamm/o Breast Lact Lact/o, lact/i Milk Galact Galact/o milk Activity 5 Build words which mean; 1. Technique of x-raying a breast _________________________________________ 2. Surgical repair of breast _______________________________________________ 3. Removal of a breast _______________________________________________ Write the meaning of; 4. Lactiferous ______________________________________________________ 5. Prolactin ______________________________________________________ 6. Galactorrhoea ______________________________________________________ Obstetrics Page 4 of 6 Abbreviations: ARM Artificial rupture of membranes CTG cardiotocograph DOB Date of birth EDC/D Estimated date of confinement/delivery EDD Estimated date of delivery EP Ectopic pregnancy FDIU Foetal distress in-utero FECG Foetal electrocardiograph FHR Foetal heart rate HDN Haemolytic disease of the newborn IUD Intra-uterine death/intra-uterine device LSCS/LUSCS Lower section caesarian section NB Newborn PET Pre-eclamptic toxaemia PPH Postpartum haemorrhage PROM Premature rupture of membranes PV Per vaginum, per vagina Apgar score Method of assessing the general state of a baby one and five minutes after birth. Named after Virginia Apgar. Appearance (colour), pulse (heart rate), grimace (response to slap), activity (movement), respiration (breathing). Two points for each, a score of 8 - 10 indicates a baby in excellent condition, a score of 7 or less would cause concern. Caesarean section delivery of the foetus through an abdominal incision episi/o pubic region, vulva gravida a pregnant woman multigravida woman who has been pregnant at least twice multipara a woman who has given birth to two or more children -natal pertaining to birth nulligravida having never been pregnant para to bear; a woman who has produced one or more viable offspring primigravida first pregnancy primipara first delivery the period of up to about 6 weeks after childbirth during which the uterus returns to normal size (involution). puerperium Obstetrics Page 5 of 6 MISCARRIAGE Expulsion of products of conception before 20 weeks gestation. Woman who has had 3 consecutive pregnancy losses before 20 weeks gestation with foetuses under 500 grams. Spontaneous abortion Expulsion of the products of conception occurring naturally Habitual aborter Incomplete Inevitable Missed Threatened Part of the foetus or placenta is retained within the uterus One which has advanced to a stage where termination of pregnancy cannot be prevented. Cervix is opened. Early signs and symptoms of pregnancy disappear and the foetus dies, but is not expelled for some time. Abdominal pain and bleeding from the uterus but the foetus is still alive. Cervix is closed. Conditions and Terms: Cervical incompetence Ectopic pregnancy Placenta praevia Pre-eclampsia Obstetrics Abnormal weakness of the cervix which can result in recurrent miscarriages Pregnancy that develops outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tubes Placenta situated in the lower part of the uterus, near or over the cervix Serious condition in which hypertension, oedema and proteinuria develops in a woman during the second half of pregnancy Page 6 of 6