* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SAT ACT The Exterior Angle Theorem
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
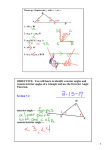
SAT / ACT GEOMETRY Triangle The Exterior Angle Theorem An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two interior angles remote from it. Example 1 Find the measure of the exterior angle. Solution By Exterior Angle Theorem, find z: z = 50° + 84° = 134°. Example 2 Find the measure of the exterior angle labeled x for the isosceles triangle. Solution 1). From ∆EFG find the values of angles ∠F and ∠E. m (∠F) = m (∠E) = 180° − 118° 2 = 31°. 2) By Exterior Angle Theorem find x = m (∠HEF). x = m (∠F) + m (∠D) = 31° + 118° = 149° Example 3 Find the measure of ∠X. Solution 1) ∆VUW is an isosceles triangle, therefore m (∠VWU) = m (∠V) = 50°. 2) ∆XWU is an isosceles triangle, therefore m (∠WUX) = m (∠X). 3) ∠VWU is an exterior angle of the triangle XWU and is equal to the sum of the measures of the two remote interior angles: m (∠VWU) = m (∠WUX) + m (∠X) ⇒ 50° = 2m (∠X) ⇒ m (∠X) = 25° Example 4 In the figure below, find the measure of x. Solution m (∠ EDF) = 50°, and m (∠ DFE) = 180° − 110° =70°. Angle x is an exterior angle of the triangle DEF and is equal to the sum of the measures of the two remote interior angles: x= 50º + 70º = 120º