* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Cycle
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
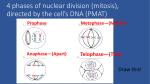
Cell Division Cell Cycle Cells divide to make new cells Includes interphase and all of the stages of mitosis Diploid Cell Normal cells o (e.g. skin cells, heart cells, etc) Cell goes through mitosis 1 round of cell division makes 2 exact copies of itself (identical) o Daughter cells have same number of chromosomes as parent (e.g. 46 chromosomes in humans) Haploid Cells Goes through two rounds of cell division Has only ½ of the chromosomes of the parent cell o e.g. 23 chromosomes instead of the 46 chromosomes of a human parent cell End with four cells, ½ the chromosomes in each cell Gametes (sex cells) Chromatids DNA & assorted proteins Dispersed in nucleus Not seen until the cell divides (then called chromosomes) Chromosomes Chromatids that have combined Visible during division DNA & assorted proteins Each strand is a sister chromatid Held together by a centromere Gene Part of a chromosome Regulates the characteristics present in an individual Mitosis (diploid cells) Interphase Cell is not dividing Going through normal cell functions Prophase Chromosomes double and become visible Nuclear membrane disappears Centrioles appear o Act as anchors as the cell divides Spindle fibers start to form from the centrioles o Act as fishing line Metaphase Chromosomes line up o Normally in the middle of the cell Spindle fibers attach to chromosomes Anaphase Chromosomes split in half Spindle fibers contract o Reeling in the fish Sister chromosomes pulled to different poles of cell Telophase Cytokinesis o Cytoplasm splits Animal cells = pinches in two Plant cells = forms a cell wall down the center of the cell Nuclear membrane reforms Centrioles and spindle fibers disappear Mitosis End Result Two daughter cells Identical to each other and to the original parent cell Diploid cells, same number of chromosomes as the parent cell Meiosis (haploid cells) InterphaseI Cell is not dividing Going through normal cell functions Prophase I Chromosomes double and become visible Nuclear membrane disappears Centrioles appear o Act as anchors as the cell divides Spindle fibers start to form from the centrioles o Act as fishing line MetaphaseI Chromosomes line up o Normally in the middle of the cell Spindle fibers attach to chromosomes Anaphase I Chromosomes split in half Spindle fibers contract o Reeling in the fish Sister chromosomes pulled to different poles of cell TelophaseI Cytokinesis o Cytoplasm splits Animal cells = pinches in two Plant cells = forms a cell wall down the center of the cell Nuclear membrane reforms Centrioles and spindle fibers disappear Meiosis I End Results Two identical cells Will go under another round of cell division InterphaseII Cell is not dividing DNA is not duplicating Prophase II Occurring in two cells at the same time Chromosomes double and become visible Nuclear membrane disappears Centrioles appear o Act as anchors as the cell divides Spindle fibers start to form from the centrioles o Act as fishing line MetaphaseI Occurring in two cells at the same time Chromosomes line up o Normally in the middle of the cell Spindle fibers attach to a single chromatid o Not the entire chromosome as in mitosis Anaphase I Occurring in two cells at the same time Chromosomes split in half Spindle fibers contract o Reeling in the fish Sister chromatids pulled to different poles of cell TelophaseI Occurring in two cells at the same time Cytokinesis o Cytoplasm splits Animal cells = pinches in two Plant cells = forms a cell wall down the center of the cell Nuclear membrane reforms Centrioles and spindle fibers disappear Meiosis End Result Four daughter cells Goes through two rounds of cell division Has only ½ of the chromosomes of the parent cell o e.g. 23 chromosomes instead of the 46 chromosomes of a human parent cell End with four cells, ½ the chromosomes in each cell Gametes (sex cells) o Now can share genetic information