* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide for Final Laboratory Exam
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
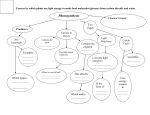
STUDY GUIDE FOR LAB FINAL (SPRING 2003) *** This study guide covers the main points from each lab. You should use this along with your quizzes and notes from lab to study. When you are studying the terms and key points, relate everything to the activities we did in each lab!! **DON’T FORGET the slides we looked at and anything that was on the back counter. Photosynthesis VOCABULARY IN LAB BOOK Review your electromagnetic spectrum: between what wavelengths does visible light fall? In the whole spectrum, does visible light fall in an area of high or low energy? Know which end of the whole spectrum has long wavelengths, short wavelengths, high energy, and low energy; why is light important to Earth’s system? Are colors in our world due to reflection or absorption of light? Why are pigments so important? What are the four types of pigments we talked about in class? What role do each type play in photosynthesis? Know the overall reaction of photosynthesis: where in the cell does it occur? What are the inputs? What are the outputs? How does the light reaction differ from the Calvin Cycle? Where does each occur? Where does the output oxygen come from? Where does the output glucose come from? What does a plant do with the glucose if it is not needed immediately? How does photosynthesis relate to cellular respiration? Review the experiments we did in class (light intensity, starch production) Patterns of Inheritance and DNA technology VOCABULARY IN LAB BOOK What is the process of cellular division that produces gametes? What types of things can cause genetic variation during this process? What is phenotype? What is genotype? What are genes? What is an allele? Know the difference between homozygous and heterozygous, dominant and recessive. Be able to do a monohybrid cross using a punnet square: be able to determine ratios of your cross. Why is DNA fingerprinting so important? What is the role of restriction enzymes? What is gel electrophoresis used for? Do all DNA fragments move down the gel at the same speed? If asked to, how would you go about reading a gel? Natural Selection-Animal Feeding Adaptations VOCABULARY IN LAB BOOK Be able to explain the process of natural selection: are we talking population or individual? How does evolution fit into this concept? What is reproductive success? What are inherited traits? How do they differ from “acquired traits”? How do feeding adaptations fit into the picture? How do they help with an organism’s “success”? We looked at feeding behavior in Hydra: what two steps needed to happen in order for the hydra to get a tasty meal? What is a chemical elicitor? How did the dentition of the animal skulls reflect their probable diet type? How did the bird beaks/features reflect their probable diet type? Population Ecology VOCABULARY IN LAB BOOK What is a population? What is population ecology? What kinds of things (environmental pressures) can limit population growth? What kinds of limiting factors are densitydependent? What kinds of limiting factors are density-independent? What is carrying capacity? What is the difference between exponential growth and logistic growth? What kinds of organisms display exponential growth? What kinds of organisms display logistic growth? We used E.coli in our population experiment: what kind of generation time did this organism have? How does this bacterium reproduce? It is a facultative anaerobe: what does this mean? How can antibiotics affect a bacterial population’s growth? How can predation affect a population’s growth? What was the function of the spectrophotometer? Review the graph of our bacterial population growth experiment: be able to discuss what is happening with each group. Community Ecology VOCABULARY IN LAB BOOK What is a community? How does a community differ from a population? How can species richness and species abundance affect the structure of a community? What is community stability? How can it affect community structure? Interspecific interactions can also have an effect on communities: what is the competitive exclusion principle? What kind of role does predation play in a community? How do the adaptations of predators and prey affect this interaction? Symbiotic relationships: INQUILINISM: what is it? What kind of affect does it have on both the host and symbiont? What is an example of this relationship? PARASITISM: what kind of affect does it have on both the host and symbiont? What is an example of this relationship? COMMENSALISM: what kind of affect does it have on both the host and symbiont? What is an example of this relationship? MUTUALISM: what kind of affect does it have on both the host and symbiont? What is an example of this relationship? Why is it important for a parasite to have multiple hosts in its life cycle? Why would it help a parasite to be hermaphroditic? Review the examples of symbiotic relationships we had in class. Natural Selection – Leaf Morphology Why would it be beneficial for plants to have various adaptations, to be so phenotypically different? Why would it be beneficial for plants to have the variety of modifications that you observed in lab? What are some of those modifications? What is the importance of the following: flowers? Leaves? Stems? Roots? Review the different types of leaf margins, leaf venation, leaf arrangement, and leaf complexity. What is the importance of having dichotomous keys, or field guides? Think about the different environments you observed in the greenhouses: desert room, fern room, tropical room, and carnivorous plant area. Be able to talk about plants found in each area and how they have adapted to thrive in their particular environment. Ecosystem Ecology VOCABULARY IN LAB BOOK Why is it important to understand energy flow and chemical cycling in ecosystems? How do biotic and abiotic factors tie into this? How do photosynthesis and respiration help to cycle energy through ecosystems? Once organisms use the energy, where does it go? What are biogeochemical cycles? What is the difference between gaseous cycles and sedimentary cycles? Be able to describe the cycles and their importance that we talked about in class: water cycle, carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, and phosphorous cycle. How has human activity impacted these cycles? Pollution plays a major role in ecosystems – review the activities from lab on simulating acid rain and eutrophication.