* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sea Floor Mapping Lesson Plan Part 2
Atmospheric lidar wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
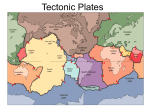
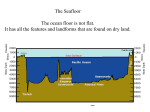
What’s Really Under the Ocean? Sea Floor Mapping, Part 2 Summary The ocean has many topographical features on land and under the ocean. Key Concepts National Science Standards Lithospheric plates on the scales of continents and oceans constantly move at rates of centimeters per year in response to movements in the mantle. Major geological events, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain building, result from these plate motions. Land forms are the result of a combination of constructive and destructive forces. Constructive forces include crustal deformation, volcanic eruption, and deposition of sediment, while destructive forces include weathering and erosion Background Information: The Earth is made of solid land. Some of the land is located above Earth’s water and some is located below the oceans. However, there are similarities and differences between the landforms found on the continents and those found on the ocean floor. Description Low land between hills or mountains Deep valley with high steep sides An underwater volcano Land which rises high above the ground Wide, flat areas of land Continental and Oceanic Landforms Continental Valley Oceanic Rift Canyon Trench Volcano Mountain Seamount ridge Plains Abyssal plains Resource: South Carolina Science Standards Support Documents, http://ed.sc.gov/agency/pr/Standards-and-Curriculum/old/cso/standards/science/sd.html Scientist use tools to map or survey the ocean floor. LIDAR is an aircraft-based sensor that uses a laser to bounce light off land. LIDAR stands for LIght Detection And Ranging. LIDAR sends laser light from the bottom of an airplane to the sea floor. The light reflects back to the airplane. LIDAR measures the time it takes for the reflections to return to the airplane. 1 Sonar systems send sound waves from the bottom of a ship to the bottom of the sea. These sound waves bounce off the sea floor and back up to the ship. SONAR stands for SOund NAvigation and Ranging. Two types of mapping the ocean floor are single-beam sonar and mult-beam sonar. Single-beam sonar have with a transceiver (transducer/receiver) mounted to the hull, or sidemount, to the ship and measures the water depth directly beneath the research vessel. The hull-mounted transceiver transmits a high-frequency acoustic pulse in a beam directly downward into the water column. Acoustic energy is reflected off the sea floor beneath the vessel and received at the transceiver Multi-beam sonar uses a swath out to each side to get full coverage of the ocean floor, with much greater detail than the lines of depth seen by a single-beam sonar. Objectives Observe, classify, and identify ocean floor features. Materials Sonar image cards set (rift, trench, seamount, volcanic island , & ridge) Classification data sheets 1-6 Classification data sheet (teacher version, answer sheet) Vocabulary word cards (rift, trench, seamount, volcanic island , & ridge) Ocean Floor Features Map Image Procedure 1. Review landforms features on land (continental) from previous learning (valley, canyon, volcano, mountain, and plains). 2. Divide your class into small groups. Photo copy enough sonar image card sets for each group. 3. Have students observe and discuss the characteristics of each image. 4. Classify images by oceanic features. Use one classification data sheet per group. 5. After the students classify the images under the specific descriptions of the ocean floor features, use the vocabulary word cards to label each column. Identify sonar image cards with vocabulary cards. Additional Activity: Ocean Floor Charades Have a student select a sonar image card of ocean floor feature. Student will act out the ocean floor features. Assessment Ocean Floor Features Map Image….Have students observe the images of the ocean floor. Have students write rift, trench, seamount, ridge, or abyssal plain by the ocean features. Additional Resources Please list any Web sites, books, publications, or other resources that would be helpful for teachers or students preparing for this lesson. 2 Got time? If you have time before your presentation, it would be helpful for me for you to provide Relevant content standards—National Science Education Standards: http://www.nap.edu/readingroom/books/nses/html/6a.html Science skills (using the Essential Science Skills grid on the EARTH Web site: http://www.mbari.org/earth/skills.htm Ocean Literacy Standards: http://www.coexploration.org/oceanliteracy/documents/OceanLitChart.pdf 3