* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2009MentorEcologyBTe..
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
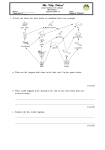
Ecology Mentor 2009 KEY (50 pts) Please mark all answers on the answer sheet provided. Make sure to write student names, school name, and team number on the answer sheet. Part I Principles of Ecology 1. Animals that only eat autotrophs are called A. Omnivores B. Producers C. Carnivores D. Herbivores 2. Grizzly bears are A. Omnivores B. Producers C. Carnivores D. Herbivores 3. Tall grasses are A. Omnivores B. Producers C. Carnivores D. Herbivores 4. A collection of interacting populations is called a A. Biosphere B. Community C. Group D. Cooperating Group 5. Which of these is an abiotic feature of an ecosystem A. Robin egg B. Potato C. Tiger D. Gravel 6-8. Identify three (3) types of Symbiosis from the following list and explain what each means. Answer must be EXACTLY correct for credit. mutualism symbioism photosynthism suppressionism commensalism parasitism predatorism Mutualism: both organisms benefit. Commensalism: one organism lives off another with no harm to host organism. Parasitism: in which organism harms its host. 9. The entire sequence of ecological communities successively occupying an area from the initial stage to the climax community is called A. rees B. sree C. sere D. rese 10. A food web is all about A. the interactions of animals B. eating C. predator and prey D. the transfer of energy 11. Primary succession starts A. with rain B. after a fire or flood C. with grass D. when there is no soil 12. Which food chain is accurate? A. snake --> mushroom --> grasshopper --> frog --> grass B. mushroom --> snake --> grasshopper --> grass --> frog C. grass --> grasshopper --> frog --> snake --> mushroom D. grasshopper --> grass --> frog --> snake --> mushroom 13. What is the highest level of consumer included in this food web? Tertiary 14. What trophic level is the grass (two words)? primary producer 15. How many top predators are depicted on this food web? 1 16. What trophic level EATS the snake after it dies (vultures, worms)? detrivore 17. curve “a” is most likely to represent the population growth of A. lions B. sparrows C. mosquitos D. cows 18. curve “b” is most likely to represent the population growth of A. chimpanzees B. bluegill C. mice D. frogs 19. Which species is r-selected? a 20. A climax community is the most A. stable B. likely to disappear C. recognizable D. common 21-25. List the 5 major ecological levels in order starting with the most specific level. Answer must be EXACTLY correct for credit. Individual Population Community Ecosystem Biosphere Part II Deserts & Grasslands 26. Which list of North American grassland types is most accurate? A. Prarie, Tall-grass, Savannah, Mid-grass, Short-grass B. Prarie, Short-grass, Tall-grass, Savannah, Bluegrass C. Medium-grass, Prarie, Tall-grass, Savannah, Short-grass D. Prarie, Fieldgrass, Savannah, Mid-grass, Short-grass 27. Grasslands are generally known for A. Hot summers and mild winters B. Mild summers and winters C. Hot summers and cold winters D. Mild summers and cold winters 28. What is the most important identifying mark of a desert? A. elevation B. temperature C. cacti D. rainfall 29-32. What are the 4 major North American desert regions? Great Basin Mojave Sonoran Chihuahuan 33. Which North American desert region is a cold desert? Great Basin 34. What is the indicator species of the cold desert? Sagebrush 35. What desert reptile is famous for eating rattlesnakes? Kingsnake 36. What Brazilian invasive species is identified by the acronym RIFA? Red imported fire ants 37. What is the common name of the most venemous desert scorpion? Bark Scorpion 38. Which of the following is a wind formed desert feature? A. hoo doo B. yoo doo C. doo yoo D. koo koo 39. What is the steep side of a sand dune called? slip face 40-41. Besides climate, what 2 things keep the grass in check (natural lawnmowers)? grazing fire 42. What is the range of prarie precipitation (inches)? A. 8-16 B. 12-22 C. 16-24 D. 20-28 43. What is a great grassland indicator species? A. Bald Eagle B. Prarie Rattlesnake C. Jackrabbits D. Prarie Dogs 44. How many grassland national parks are there in North America? 0 45-47. Name the three broadest categories of North American grassland by vegetation. Tall-grass Mixed Grass Short-grass 48. What is the most common way for desert animals to escape the heat? underground 49. What venemous lizard is found in North American deserts? Gila Monster 50. What is the only North American wild pig? Javelina