* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam I - Chemistry With BT
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
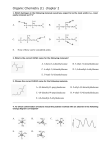
Name: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (CHEM 323) EXAM 1 September 22, 2015 There are five pages, TEN questions, and a total of 114 points in this exam, which gives an extra 14 points on top of that required for a “perfect” paper. Please read each question carefully and possibly more than once. Good luck… (10) 1. Draw Lewis structures for the following ions. Show all carbons, hydrogens, and lone pairs. 1.1. 1.2. (12) 2. In each of the compounds below identify the overlapping orbitals in the bond indicated by an arrow. 2.1. 2.2. Question submitted by Maria (8) 3. Give the IUPAC name of the following branched alkane: 3.1. How many signals are detected in the 13C NMR of the molecule above? (13) 4. The Newman Projection given below represents a portion of the substituted cyclohexane shown in its chair form. 4.1. In the Newman Projection above identify the atom with the question mark (as referenced in the chair structure) 4.2. Draw a Newman Projection representation of the same portion of the cyclohexane but for the conformation below: 4.3. Circle the more stable cyclohexane conformation. 4.4. Give a narrative explanation of your answer for 4.3 based on the Newman Projections (the one given above and the one you provided for 4.2). (7) 5. Write the missing resonance structure consistent with the electron movement indicated by the curly arrows. Show all lone pairs and formal charges (if any) Page 2 Inspired by question from Toni (8) 6. Four constitutional isomers of C7H16 are given below. However there are several further constitutional isomers which are not shown. Give the two of the missing constitutional isomers. (15) 7. In a project to determine and compare fuel efficiency, researchers carry out complete combustion experiments on cis-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane and on trans-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane. However, instead of writing everything in their lab note-books, they tabulate it on a sheet of paper, which subsequently goes missing. They do remember the H(combustion) values to be different for their samples. In order to help the researchers, please construct the energy diagram below filling the boxes with the appropriate reactants and/or products. E Hocomb 7.1. Give a narrative explanation to rationalize the results. You may need to write distinguishable conformations of the reactants to validate your argument. Page 3 (17) The 13C NMR spectra of two alcohols are given below. Either alcohol can function as an acid. 8. The statements below are “True” or “False”. Place the letters T or F in the blank underlined space before each statement. 8.1. 8.2. ____ The electron density of the carbon at 79.2 ppm (for the second alcohol) is higher than that of the carbon at 65.0 ppm (for the first alcohol) . ____ The two signals around 80 ppm in the second spectrum show the presence of resonance effect. ____ The signal at 79.2 ppm shows that the chlorine atoms are influencing the electron density of the oxygen bearing carbon (the one indicated by the arrow) as well. ____ The signal at 79.2 ppm demonstrates the inductive effect of the chlorine atoms. ____ The signal at 79.2 ppm indicates that the conjugate base for the second alcohol will be able to delocalize the charge more effectively. ____ The first alcohol is a stronger acid than the second alcohol. Draw the structure of the conjugate base for each alcohol. Circle the more stable conjugate base. Page 4 Inspired by question from Kealina (12) 9. In the boxes under the structures given below write “1” for the molecule with the highest boiling point and “4” for the molecule with the lowest boiling point. 9.1. What type of intermolecular force is needed to be overcome in order to bring the most volatile molecule to boiling? 9.2. What type of intermolecular force remains to be operating once the least volatile molecule is in the gas phase? (12) 10. Circle the best possible correct answer (only one) for the following multiple-choice questions: 10.1. The extent to which an acid is capable of releasing a hydrogen ion illustrates (1) (2) (3) (4) 10.2. its volatility the magnitude of its dissociation constant its ability donate electrons all three answers are correct. Which of the following is the electron configuration of an element which forms a neutral molecule without completing its octet? (1) 1s2 2s2 2p1 10.3. (2) 1s2 2s2 2p2 (3) 1s2 2s2 2p3 (4) 1s2 2s2 2p4 The element in 10.2 can function as a (1) nucleophile (2) base (3) Lewis acid (4) carbene Question submitted by Milton 10.4. The reason why the following conformation is not the most stable spatial arrangement is because it experiences destabilizing interactions referred to as (1) hydrogen bonding (2) steric strain (3) torsional strain (4) angle strain (5) The conformation above is the most stable spatial arrangement. Page 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 TOT 10 12 8 13 7 8 15 17 12 12 0 0 114 Page 6