* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam 6A Sectionalism 1845-1860
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
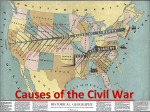
Practice Test Antebellum America 1. By the 19th Century, (A) most southerners owned slaves (B) the smaller slaveowners owned a majority of the slaves (C) most slaves lived on large plantations (D) slavery was a dying institution. 2. The most pro-Union of the white southerners were (A) “poor white trash” (B) mountain whites (C) small slaveowners (D) non-slaveowning subsistence farmers. 3. Northern attitudes towards free blacks can be best described as (A) supporting their right to full citizenship (B) supporting black voting (C) advocating black movement into the new territories (D) most Northern whites did not care much for blacks 4. The clash between Preston S. Brooks and Charles Sumner revealed (A) the seriousness of political divisions in the North (B) how important honor was to Northerners (C) that despite divisions over slavery, the House of Representatives would unite to expel a member for bad conduct (D) how dangerously inflamed passions were becoming over slavery in the North and South. 5. The South became the Cotton Kingdom in the early nineteenth century because of (A) Eli Whitney’s invention of the cotton gin (B) the new profitability of shortstaple cotton (C) the opening of rich river bottomlands in the Gulf Coast states (D) all of these. 6. In ruling in Dred Scott v Sanford (1858), the United States Supreme Court (A) hoped to promote further debate on the slavery issue (B) ruled that Scott was not free (C) supported the concept of popular sovereignty (D) reunited the Democratic Party. 7. Even those who did not own slaves in the pre-Civil War South supported that institution because they (A) dreamed of someday owning slaves themselves (B) presumed themselves racially superior to black slaves (C) were afraid of being overwhelmed by the black race (D) all of these. 8. In the 1840s, the view that God had ordained the growth of an American nation stretching across North America was called (A) continentalism (B) isolationism (C) Anglophobia (D) Manifest Destiny. 9. In 1846, the United States went to war with Mexico for all of the following reasons except: (A) Manifest Destiny (B) the deaths of American soldiers at the hands of Mexicans (C) Mexican objections to the admission of Texas to the Union (D) end slavery in Mexico 10. During the Mexican War, the Polk administration was several times called upon to respond to “spot” resolutions indicating where American blood had been shed to provoke the war. The resolutions were frequently introduced by (A) Abraham Lincoln (B) Henry Clay (C) Robert Gray (D) David Wilmot. 11. The United States’ victory in the Mexican War resulted in (A) renewed controversy over the issue of extending slavery into the territories (B) a possible split in the Whig and Democrat Parties over slavery (C) Mexico relinquishing an enormous amount of land to America (D) all of the above. 12. The Wilmot Proviso introduced into Congress during the Mexican War declared that (A) Mexican territory would not be annexed to the United States (B) slavery would be banned from all territories Mexico ceded to the United States (C) the United States should annex all of Mexico (D) the United States should have to pay Mexico a financial indemnity for having provoked the war. 13. Those people most opposed to President James K. Polk’s expansionist program were the (A) western Democrats (B) antislavery forces (C) Senate Democrats (D) supporters of John C. Calhoun. 14. The principle of “popular sovereignty” would have the question of slavery in the territories determined by (A) the vote of the people in any given territory (B) a national referendum (C) congressional legislation (D) a Supreme Court decision. 15. In the 1844 presidential election, (A) Polk won by promoting Manifest Destiny (B) slavery was outlawed (C) the Whigs nominated Davy Crockett (D) Polk won because he promised to end the war with Mexico 16. By 1850, the South (A) was more populated than the North (B) feared that slavery might be abolished in states where it already existed (C) had more electoral votes than the North (D) had most of the US’ industry 17. President Zachary Taylor unknowingly helped the cause of compromise in 1850 when he (A) led an invasion of Texas to halt its attempts to take part of New Mexico (B) supported fellow Southerner John C. Calhoun’s plan for union (C) died suddenly and Millard Fillmore became president (D) ushered in a second Era of Good Feelings. 18. In the Compromise of 1850, Congress determined that slavery in the New Mexico and Utah territories was (A) to be banned (B) protected by federal law (C) to be decided by popular sovereignty (D) to be ignored until either territory applied for admission to statehood. 19. The fatal split in the Whig party in 1852 was over the issue of (A) the nomination of General Winfield Scott or Daniel Webster (B) slavery (C) protective tariffs (D) homestead laws. 20. Many northern states passed “personal liberty laws” in response to the Compromise of 1850’s decision on (A) slavery in the District of Columbia (B) slavery in the territories (C) runaway slaves (D) the interstate slave trade. 21. Stephen Douglas promoted the Kansas-Nebraska Act because (A) he wanted to end slavery in Nebraska (B) he wanted to promote a railroad to the west coast which would begin in Illinois (C) he wanted to end slavery in Nebraska (D) Mexican leader Santa Anna agreed to contribute money for a transcontinental railroad. 22. Stephen A. Douglas proposed that the question of slavery in the Kansas-Nebraska Territory be decided by (A) popular sovereignty (B) making Kansas a free territory and Nebraska a slave territory (C) the Supreme Court (D) admitting both California and Kansas-Nebraska to the Union. 23. The Kansas Nebraska Act led to (A) civil war in Kansas (B) a ban on slavery west of the Mississippi (C) the admission ofKansas to the Union as a slave state (D) the destruction of the Republican Party 24. After John Brown’s raid on Harpers Ferry, the South concluded that (A) it was an isolated incident (B) the North was dominated by “Brown-loving” Republicans (C) Brown should be put in an insane asylum (D) Brown had been attempting to defend his right to own slaves. 25. The scene depicted above I is the beating of Charles Sumner by Preston S. Brooks II is blatant Northern propaganda, revealing the bias of the Northern press III is an accurate depiction of the incident IV the incident, and the reaction, showed how seriously of the Nation was divided (A) (A) I only (B) (B) I & II (C) (D) II & III I, III, & IV 26. At the beginning of the Civil War, the North had all of the following advantages over the South except: (A) more manpower (B) more industry (C) stronger consensus concerning war aims (D) an established government recognized by all countries (E) making government more directly responsible to the electorate. 27. Which is the correct order chronology of these inventions? (A) Reaper, steamboat, telegraph , cotton gin (B) Cotton gin, steamboat, reaper, telegraph (C) Steamboat, cotton gin , telegraph, reaper (D) Cotton gin, reaper, steamboat, telegraph (E) Cotton gin, steamboat, telegraph, reaper 28. Which of the following can be verified by the map above? I The greatest percentage of slaves resided in the Deep South II Kentucky was not a cotton producing area III Virginia was not a cotton producing area IV The Florida panhandle was not a prime area for slavery V South Carolina had the greatest percentage of cotton and slaves (A) I only (B) III only (C) IV only 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. C D D A D B D D D A D B B A A B C C B C B A A B D X X X (D) (E) II only I, II, III, IV & V