* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
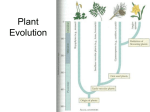
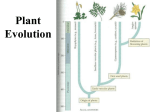
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Exam 3 Review Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Course: Instructor: Date: Kelly Biol 211 (1) Roe 02/24/15 1. During the bryophyte life cycle, the _____ is dependent on the _______. a) sporophyte, gametophyte b) gametophyte, sporophyte c) sporangium, gametophyte d) gametophyte, sporangium e) none of the above 2. In plants, a ___________ produces gametes, while a __________ develops from a zygote. a) sporophyte, sporophyte b) gametophyte, sporophyte c) sporangium, gametophyte d) archegonium, gametophyte 3. Which of the following is not true about alternation of generations? a) occurs in all sexually reproducing organisms b) is the alternation of two multicellular body forms (gametophyte, sporophyte) c) produces both zygote and spores d) includes both mitosis and meiosis 4. The transition from an aquatic to terrestrial environment had a lot of challenges for the first land plants. Which of the following was not a problem for the first land plants? a) sources of water b) sperm transfer c) desiccation d) herbivores 5. What is the closest relative to land plants? a) Rhodophyta, because both clades have cellulose cell walls. b) Euglenozoa, because both clades have green chloroplasts. c) Charophyceans, because both clades have rose-shaped complexes that synthesize cellulose. d) Oomyctes, because both clades have cellulose cell walls. e) Archaea, because both clades are autotrophic. 6. Globally, 80% of all the calories consumed by humans come from ___ species of angiosperm crop plants. a) 3 b) 6 c) 10 d) 20 e) humans don’t eat angiosperms 7. This Phylum contains the mushrooms, puffballs, and shelf fungi A) Zygomycota B) Ascomycota C) Basidiomycota D) Glomeromycota E) Chytridomycota 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu 8. The bodies of most fungi are_________ A) composed of hyphae B) referred to as a mycellium C) usually underground D) A and B only E) A, B, and C 9. Fungal cells can reproduce asexually via mitosis. Many fungi can also reproduce sexually by undergoing A) plasmogamy followed by karyogamy B) dispersal followed by germination C) karyogamy then meiosis D) germination then dispersal 10. Which of the following do all fungi have in common? A) sexual life-cycle B) symbiosis with algae C) absorbtion of nutrients D) coenocytic hyphae E) a basidiocarp 11. Following the life of an Ascomycete from ascospore to ascocarp, what is the order of the ploidy –level observed. A) dikaryotic, haploid, diploid, dikaryotic B) diploid, haploid, dikaryotic, diploid C) haploid, dikaryotic, diploid, haploid D) haploid, diploid, haploid, diploid E) none of the above 12. The association between plant roots and soil fungi is best described as A) parasitism B) mutualism C) predation D) detrimental E) beneficial only to one of the pair 13. What are the sporangia of the bread mold Rhizopus? A) Asexual structures that produce haploid spores B) asexual structures that produce diploid spores C) sexual structures that produce haploid spores D) sexual structures that produce diploid spores E) vegetative structures with no role in reproduction 14. Both fungi and animals are heterotrophic. The difference between the two is that animals get their nutrition A) from organic matter B) by using enzymes to digest their food C) by ingesting their food D) by consuming only live prey E) by preying only on animals Plants Become Terrestrial: When: Closest Protist Relative: Cell Wall Composition: 4 plant advantages to life on land : 4 ways the environment changed: What does it mean to be vascular? Nonvascular? Plant Groups are Diverse: Nonvascular and Seedless Vascular and Seedless Vascular with Seeds Ex. Anthocerophyta (hornworts) For the above groups does the gametophyte or sporophyte dominate? Gymnosperms vs. Angiosperms: Which undergoes Double Fertilization? Depict the Seeds: Naked Seed Ovules develop into___________________. Ovary develop into___________________. What is pollination vs. fertilization? Covered Seed Plant Lifecycles: Alteration of Generations We may or may not complete this page during the review. However, it is a great study tool! 1. What is growing? 2. Add in Ploidy 3. Where are meiosis and fertilization occurring? Does pollination occur? 4. Any special structures? 5. What dominates? How does the lifecycle change? Nonvascular Seedless (Bryophytes): Vascular and Seedless (Ferns): Vascular with Seeds (Gymnosperm): Vascular with Seeds (Angiosperms): FUNGI: How do they Obtain Food? Significance? Cell Wall Composition: Structure: Define and Label: HyphaeFruiting BodyMyceliumWhere can spores be found(2 places) Septate: Class: Sexual vs. Asexual: Septate vs. Aseptate: Fruiting Body Name and Ploidy: Dominant Mycelium Ploidy: # of Spores: Examples: Aseptate or Coenocytic: Zygomycota Ascomycota Basidiomycota Diverse Lifestyles: How are these important to humans? 1. 2. 3. 3 Differences between Fungi and Fungi-like protists (Oomycetes): PLANTS When did they become terrestrial? Closest protist relative? 4 Protist and Land Plant shared Characteristics 4 reasons why a terrestrial environment was advantageous 4 ways land plants changed the terrestrial environment 5 shared characteristics between plants and closest protist relative (more in depth than the 4 above) 5 differences all land plants share -apical meristems -Alternation of Generations * -Walled spores in sporangia * -multicellular gametangia * -multicellular dependent embryo * **These are easier to understand after looking at lifecycles Cuticle Secondary Compounds Plant Ecological significance Pollination and Dispersal Methods Nonvascular vs. Vascular and Seedless vs. Seeded Plants (know which phylums are in each group) 3 things vascular plants have over nonvascular plants PLANT LIFECYCLES! (The differences between Moss(Bryophyte), Fern(Pterophyte), Pine (Gymnosperm), and Flowers (Angiosperm) -Antheridia and Archegonia (Male vs. Female) -Gametophyte and Sporophyte (Which dominates? When are they nutritionally dependent/independent) -Sporangia and Gametangia -Meiosis and Mitosis (When does Meiosis occurs?) -Ploidy( N, 2N, and 3N) - Fertilization (Which need water) and Pollination (What makes these different?) - Xylem and Phloem -Roots , Leaves (Sporophylls), -Megaspores and Microspores (Male v. Female) Mega/Micro sporangium -Strobilus and Sori -Zygote and Embryo -Heterosporous -Ovules and Ovary (Which becomes fruit and which becomes seeds?) -Seed structure Angiosperm and Gymnosperm (3 generations) ( Which has endosperm?) -integuments and micropyle Dicots and monocots Oogamus 3 advantages angiosperms have over gymnosperms FUNGI- (focus on these classes: Zygomycota, Ascomycota, and Basidiamycota) Heterotroph Puffballs, Morels, Truffles, Molds, Stinkhorns, etc. (What Class?) How they obtain food (Importance of Surface Area?) The Diverse Lifestyles Hyphae, Mycelium, Fruiting Body What are their cell walls made of? What are plant cell walls made of? Septate vs. Aseptate=Coenocytic Specialized hyphae = hoop traps and haustorium Mycorrhiza FUNGI LIFECYCLE! (Know how the cycles are different) -Sexual and Asexual -Plasmogamy and Karyogamy -Ploidy (N, 2N and N+N) (Which dominates?) -How many sexual spores do each form? Fungus the good and the bad Ecological Importance and their diverse lifestyles Human Uses Differences Between Fungi and Fungi-like protists