* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
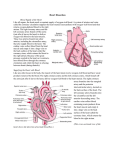
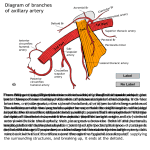
Dr. Pardeep Kumar They are the vessels that carry the blood away from the heart. Walls of arteries are strong and elastic. The wall of artery made up of 3 layers:1-Tunica intima (inner) 2-Tunica media (middle) 3-Tunica adventitia (outer) Origin :- Pulmonary orifice of Rt ventricle Course :- runs upward & backward Level :- 5th Thoracic vertebrae Branches :1-Right Pulmonary Artery 2-Left Pulmonary Artery Longer & larger than left aretry. Course :- runs horizontally to right Braches :- it has 3 braches which supply superior, middle and inferior lobes of lungs Shorter and smaller than right artery Course :- runs horizontally to the left side Branches : it gives 2 branches for superior and inferior lobes of left lung. Aorta It is great arterial trunk It receives oxygenated blood from Lt. Ventricle & distributes to all parts of the body. It has 3 parts Ascending Aorta Arch of Aorta Descending Aorta Descending Thoracic Aorta Abdominal Aorta Ascending Aorta It arises from upper end of Lt. Ventricle 5 cm long & enclosed in Pericardium It begins from lower border of 3rd costal cartilage It runs upwards forwards & to right & becomes continuous with arch of aorta at sternal angle The roots of Aorta has 3 dilatations of vessel wall called aortic sinuses They are anterior, left posterior & Rt. Posterior Branches Rt. Coronary artery from anterior aortic sinus Lt. Coronary Artery from Lt. Posterior aortic sinus Arch of the Aorta It is continuous of ascending aorta It is present in superior Mediastinum The arch of aorta extends from behind Rt. border of sternum at the level of 2nd costal cartilage to Lt side of lower border of T4 It inclines from Rt to Lt & front to back It rises to a height corresponding to centre of manubrium sterni & lies in its entire course within sup mediastinum • • • • Branches Brachiocephalic trunk which divides into Rt. Common carotid & Rt. Subclavian artery Lt common carotid artery Lt subclavian artery Descending Thoracic Aorta It is continuous of arch of aorta It lies in Posterior Mediastinum Course It begins on Lt. Side from lower border of T4 vertebrae & terminates at the T12 Branches 9 Posterior intercostal arteries (3rd to 11th ) Subcostal arteries 2 Lt. Branchial arteries Mediastinal branch Pericardial branch Oesophageal branch Superior Phrenic artery Internal thoracic artery - descends into thorax 1.2cm lateral to edge of sternum, and ends at the sixth costal cartilage by dividing musculophrenic and superior epigastric arteries Brachiocephalic Trunk / Artery This is the largest branch of the arch of aorta & is about 4 to 5 cm in length Origin arises from convexity of arch of aorta , passes obliquely upward, backward & to the Rt Branches Only 2 terminal branches Rt. common carotid artery Rt. subclavian artery Abdominal Aorta Origin Continuation of Descending thoracic aorta In midline at aortic opening opposite lower border of T12 Dr, S, Chakradhar 18 Course Runs downwards & slightly left of midline Ends infront of lower border of L4, By dividing into Rt. & Lt. Common iliac artery Dr, S, Chakradhar 19 Branches Ventral Branches Coeliac trunk Superior Mesentric artery Inferior Mesentric artery Lateral branches Inferior phrenic artery Middle suprarenal artery Renal arteries Testicular or ovarian arteries Dr, S, Chakradhar 20 Dorsal Branches Luimbar arteries – 4 pairs Median Sacral artery unpaired Terminal Branches Common iliac arteries Dr, S, Chakradhar 21 Blood supply of Head & Neck is chiefly from branches of common carotid arteries and partly from subclavian arteries • Common Carotid Artery • External Carotid Artery • Internal Carotid Artery • Subclavian Artery It is a bilateral artery which supply Head and Neck. • Right CCA arise from brachiocephalic Trunk. • Left CCA arise from Aortic arch. • Course of CCA:- upward and lateral • Branches of CCA:- it gives 2 branches 1-Internal carotid artery 2-External carotid Artery • Right Common Carotid Artery: Arises from brachiocephalic artery (Behind right sternoclavicular joint) Left Common Carotid Artery: Arises from Arch of Aorta Runs upwards in the neck from sternoclavicular joint to upper border of thyroid cartilage External Carotid Artery Internal Carotid Artery Begins at the level of upper border of thyroid cartilage Terminates in the substance of the parotid gland behind the neck of mandible by dividing into: Superficial temporal artery Maxillary artery Neck Face Scalp Tongue Maxilla Superior thyroid artery 2. Lingual artery 3. Posterior auricular artery 4. Facial artery 5. Occipital artery 6. Ascending pharyngeal artery 7. Maxillary artery 8. Superficial temporal artery "sister lucy's powdered face often attracts medical students"; 1. Begins at the level of upper border of thyroid cartilage No branches in the neck Through carotid canal enters into cranial cavity Supplies brain, eyes, forehead and part of the nose Right Subclavian Artery: Arises from brachiocephalic artery (Behind right sternoclavicular joint) At outer border of 1st rib it becomes Axillary Artery Left Subclavian Artery: Arises from Arch of Aorta in the thorax Runs upwards to the root of the neck & arches laterally At outer border of 1st rib it becomes Axillary Artery Scalenus Anterior muscle passes anterior to the artery on each side and divides it into 3 parts. 1. 1st part of subclavian artery 2. 2nd part of subclavian artery 3. 3rd part of subclavian artery Extends from the origin of the subclavian artery to the medial border of the Scalenus anterior muscle. Branches: 1. Vertebral artery 2. Thyrocervical Trunk 3. Internal thoracic artery Branches: 1. Vertebral artery Spinal and muscular branches in neck Branches in skull Branches: 2. Thyrocervical Trunk Inferior thyroid artery Superficial cervical artery ( Transverse Cevvical Suprascapular artery Branches: 3. Internal thoracic artery Superior epigastric artery Musculophrenic artery Lies behind the Scalenus anterior muscle. Branches: 1. Costocervical trunk Superior intercostal artery Deep cervical artery Extends from the lateral border of the Scalenus anterior muscle to the lateral border of 1st rib. Branches: (Occasional) 1. Superficial cervical artery 2. Suprascapular artery Superficial Pulse Points- arteries, not veins temporal 60 beats/minute facial carotid brachial radial • • • • • • • • Temporal artery Facial artery Common carotid artery Brachial artery Radial artery Femoral artery Popliteal artery Posterior tibial artery • Dorsal pedis artery femoral popliteal