* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Handout/Practice Problems
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Reaction progress kinetic analysis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical imaging wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Industrial catalysts wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
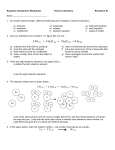
CHEMICAL REACTIONS During a chemical reaction, bonds are broken and formed as molecules and atoms combine and rearrange to form new substances. A chemical equation is a sentence that uses chemical formulas and symbols to tell us what happens during a chemical reaction. REACTANTS PRODUCTS 2H2 (g) + O2(g) → 2 H2O(l) HOW CAN YOU TELL IF A CHEMICAL REACTION IS OCCURRING? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. SYMBOLS USED IN CHEMICAL EQUATIONS Symbol Explanation + (s) or ↓ (l) (g) (aq) Catalyst Writing Chemical Equations 1. a. b. c. d. e. f. Write formulas and other symbols for these substances: metallic potassium sodium chloride dissolved in water heat supplied to a chemical reaction liquid mercury zinc chloride as a catalyst carbon dioxide gas 2. Write a skeleton equation for each of these chemical reactions: a. Aluminum metal reacts with oxygen in the air to form solid aluminum oxide. b. When solid mercury (II) sulphide is heated in the presence of oxygen, liquid mercury metal and gaseous sulphur dioxide are produced. c. Oxygen gas can be made by heating potassium chlorate in the presence of the catalyst manganese dioxide. Potassium chloride is left as a solid residue. 3. Write sentences that completely describe each of the chemical reactions shown in these skeleton equations. a. BaCl2 (aq) + H2SO4 (aq) → BaSO4 (s) + HCl (aq) b. NH3 (g) + O2 (g) → NO (g) + H2O (g) c. N2O3 (s) + H2O → HNO2 (aq) d. K(s) + H2O → KOH (aq) + H2 (g) e. NaOH (aq) + HNO3 (aq) → H2O + NaNO3 (aq) f. FeO(s) + C(s) Fe (s) + CO (g)