* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fertile Crescent
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
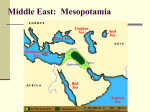
4 early River Valley Civilizations • Fertile Crescent- Tigris & Euphrates Rivers (Mesopotamia) • Egyptian Civilization - Nile River • Indian Civilization - Indus River • Ancient China - Huang He (Yellow) River PP Design of T. Loessin; Akins H.S. The Ancient Fertile Crescent The Middle East: “The Cradle of Civilization” Background Info. • Fertile Crescent- narrow strip of land between Tigris and Euphrates Rivers • Mesopotamia- “between the rivers” • 5,000 B.C.E. – 4,000 B.C.E.- Neolithic farmers built civilization Civilizations of the Fertile Crescent Sumerians Akkadians Babylonians Hittites, Assyrians, Chaldeans Persians Phoenicians & Lydians Sumerians • Settled in Sumer • Agriculture: grew crops, domesticated animals, used irrigation • Developed system of writing– cuneiform Sumerian Achievements • Architecture: – Arches – Ziggurats- temples • Other Achievements: – The wheel – Number System – Lunar Calendar Sumerian Society • Government: – City-States: town or city and the surrounding land controlled by it • Education and Religion: – Only upper-class boys – and no girls – attended school – Polytheistic: Sumerian gods were identified with forces of nature The Akkadians • Conquered Sumerians in about 2330 B.C.E. • Sargon (2334 B.C.E. to 2279 B.C.E.) – Most powerful Akkadian King – Established great empire • Lasted about 150 years but conquered by invaders The Babylonians • 1792 B.C.E. conquered the Akkadians • Hammurabi: strong ruler that came to power in Babylon – Outstanding political leader and lawmaker • Code of Hammurabi – 282 laws compiled under his direction – Punishment was harsh…based on the idea of “an eye for an eye” Hittites • Invaded from Asia Minor in 1600s B.C.E. • Conquered Babylon • Achievements: – Iron – Legal System • Only major crimes received death penalty • Pay fine rather than experience retaliation • Why unsuccessful? – Too far from their homeland to control Babylon permanently Assyrians • Dominated area of southwest Asia between 900 B.C.E. and about 650 B.C.E. ● Built large empire: expanded power across the Fertile Crescent, Mesopotamia, Syria, Palestine, and the Nile Valley (Egypt) Assyrians • Fierce, effective warriors – Chariots in battle – Cavalry- soldiers on horseback – Often enslaved people they conquered and killed captured enemy soldiers Assyrians Contd. • Assyrian King had absolute, or total, power • Library in Nineveh – Capital city – Epic of Gilgamesh- the story of a Sumerian king and one of the oldest works of literature known • Civil War: weakened Assyria so that it could not resist outside invaders Chaldeans • Nebuchadnezzar: under his leadership, conquered Assyrians and most of Fertile Crescent – Governed from the rebuilt city of Babylon from 605 B.C.E. until his death in 562 B.C.E. • Babylon and the Hanging Gardens – Once again became large and wealthy city – Trade flourished; within city impressive canals and magnificent buildings – To please one of his wives, the king planted thousands of brightly colored tropical trees and flowers on the palace grounds…became known as the Hanging Gardens, one of the Seven Wonders of the World • End of an empire – After Nebuchadnezzar’s death, Chaldeans faced many difficulties, leading to their fall Persians • Conquered Babylon in 539 B.C.E. • Persia and Media: Persians and another group, the Medes, migrated into what is now Iran – Cyrus: Persian ruler who rebelled against the Medes, ultimately capturing Babylon and the rest of the Fertile Crescent and Asia Minor • Persian Empire: stretched between the Indus River and parts of southeastern Europe • Government: – Great concern for justice, applying the law fairly, and treating the people they conquered better than earlier empires had • Persians built road system to link sprawling empire together Persians Contd. • Religion: – Zoroaster: Persian prophet that developed an influential religious philosophy during the 600s B.C.E. – Taught that on Earth people receive training for a future life; rewards vs. punishment – Central Beliefs of Zoroastrianism: • 1) the universal struggle between good and evil • 2) the idea of final judgment • Decline of the Persians: – Weak rulers: ultimately defeated by Greek forces of Alexander the Great Phoenicians • Region of Phoenicia: present day Israel, Lebanon, and Syria • Major trading region – Seaports: Tyre and Sidon – Carthage: Phoenician city in North Africa that became a major regional and trading power • Valuable Exports: lumber, gold and silver objects, glass, purple dye • Major Contribution: the Phoenician alphabet – Spread of alphabet is good example of how commerce can speed cultural diffusion Lydians • Western portion of Asia Minor (presentday Turkey) • Major Contribution: coined money – Before coins, traders relied on bartering- the exchange of one good or service for an equal good or service – Issue with barter? Limited trade – Developed a money economy